Test tube
A test tube, also called an eprouvette (French: éprouver = to test) or test tube, is a small glass container open on one side.
Test tubes are used in laboratories for chemical reactions, examinations, for storing small quantities of liquids and much more. They are manufactured in various sizes (approx. 2 to 20 cm long, diameter between 0.6 and 3 cm). A standard size in chemical laboratories is 16 cm long with a diameter of 16 mm. If required, they can be closed with plastic foils, aluminium caps, cork, rubber or plastic plugs (colloquially also called stoppers).
Test tubes with standard ground joints are also commercially available and can be closed with ground joint stoppers made of glass or plastic. Some are printed with a volume scale in millilitres.
Glasses that are to be heated in a flame (for example, over the Bunsen burner) are usually thin-walled to avoid breakage due to thermal stress. However, there are also thicker-walled ones made of refractory glass.
The price of a simple test tube in standard size (16 cm) is about 10 cents or upwards, whereby the material used and the variation play a decisive role. For example, one made of amber glass with a standard cut and olive costs between €3 and well over €10.
Test tubes are available in various shapes, for example with round, conical or straight bottom, with flanged or straight rim.
For handling, the test tube is often held in place with a test tube holder. The usual design resembles a longer wooden clothespin with a metal spring; other test tube holders are bent from wire, consist of two flat spring steel tongues set in a wooden handle, or a metal clamp with a wooden handle.
Experienced chemists clamp a test tube to the heel of the hand with the middle finger, open the screw cap or ground-glass stopper of a reagent bottle with the thumb and forefinger, hold it firmly with this (putting it down could contaminate it) and pour the liquid into the test tube. Powdered non-clotting reagents can also be poured in using this method, in which case the amount can be dispensed by tapping with the index finger of the hand holding the bottle.
When heating test tubes, the heating is regularly interrupted and the contents are shaken by briefly tapping the test tube in the middle section with the ring finger, middle finger and index finger in succession, without the liquid spilling over or burning the hot glass. The opening of the test tube is not directed towards the face in order to prevent scalding or burns as a result of a boiling delay.
Test tubes are also often placed in a test tube box (also known as a test tube stand or test tube rack).

Test tubes in a wooden test tube stand.
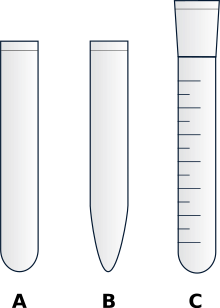
Different types of test tubes: (A) standard shape, (B) centrifuge tubes, and (C) graduated shape.

Test tubes in a stand made of coated wire.

Test tube with test tube holder
Web link
![]()
Commons: Test tube - Collection of images, videos and audio files
Questions and Answers
Q: What is a test tube?
A: A test tube is a kind of laboratory glassware, composed of a fingerlike length of glass tubing, open at the top, usually with a rounded lip at the top, and a rounded 'U' shaped bottom.
Q: What is the size range for test tubes?
A: Test tubes range in size from a couple inches to several inches long, from a few millimeters to a couple centimeters in diameter.
Q: Why are test tubes made of expansion-resistant glasses?
A: Test tubes are often made of expansion-resistant glasses, such as borosilicate glass (known by brand-names such as Pyrex and Kimax), to allow easy heating of samples, to be held in a flame.
Q: When are test tubes often preferred above beakers?
A: Test tubes are often preferred above beakers when multiple small chemical or biological samples have to be handled and/or stored.
Q: What are vacutainers?
A: Vacutainers are a type of test tube that can be used for both collection and storage of blood.
Q: What are the features of a vacutainer?
A: The features of a vacutainer are not specified in the text.
Q: Are test tubes and vacutainers the same thing?
A: No, test tubes and vacutainers are not the same thing. Vacutainers are a type of test tube that can be used for both collection and storage of blood, while test tubes are a kind of laboratory glassware designed for heating samples and storage.
Search within the encyclopedia