Bay of Biscay
![]()
This article is about the maritime area. For the Basque province, see Bizkaia.
The Bay of Biscay (![]()
![]() [bɪsˈkaːja]), also called the Bay of Biscay (French Golfe de Gascogne, Basque Bizkaiko Golkoa, Spanish Golfo de Vizcaya, Galician Golfo de Biscaia, Latin Sinus Cantabricus), is a bay of the Atlantic Ocean extending from Galicia to Brittany along the north coast of Spain and the west coast of France. This sea area is known for bad weather, strong storms, and extreme swells. The Bay of Biscay extends beyond the continental shelf due to the deep cut of the ocean. It is considered a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean.
[bɪsˈkaːja]), also called the Bay of Biscay (French Golfe de Gascogne, Basque Bizkaiko Golkoa, Spanish Golfo de Vizcaya, Galician Golfo de Biscaia, Latin Sinus Cantabricus), is a bay of the Atlantic Ocean extending from Galicia to Brittany along the north coast of Spain and the west coast of France. This sea area is known for bad weather, strong storms, and extreme swells. The Bay of Biscay extends beyond the continental shelf due to the deep cut of the ocean. It is considered a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean.
Designations
The southern Bay of Biscay, lying off the Spanish coast as far as the Adour River (France), is usually referred to in Spanish and Galician as the Mar Cantábrico (Cantabrian Sea, Latin Mare Cantabricum); the term Golfo de Vizcaya (or Golfo de Biscaia) is also used to refer to the whole of the Bay of Biscay. French also uses the term Cantabrian Sea (Mer Cantabrique) for the southern half of the Bay of Biscay, and in Basque Kantauri Itsasoa is common.
Part of Spain's Biscayan coast is known by the tourist name Costa Verde ('Green Coast'). The region has a temperate maritime climate with high rainfall, making the landscape greener than other parts of Spain.
On Mercator's 1589 map of Europe, the Bay of Biscay is designated Aquitanicus oceanus, while Cantabricus oceanus is marked west of the Spanish west coast at Cape Finisterre. The latter contradicts a synonymous use of both names.
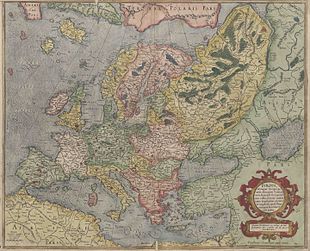
Mercator map of Europe from 1589 with the Aquitanicus oceanus
Geography
f1![]() Map with all coordinates: OSM | WikiMap
Map with all coordinates: OSM | WikiMap
Sea
The waterside boundary between the Bay of Biscay and the rest of the Atlantic is considered to be as the crow flies (geodetic great circle) from Spain's Cabo Ortegal (44° N, 8° W43.77222222-7.86805555556) or from Estaca de Bares, a few kilometres to the east, (44° N, 8° W43.790277777778-7.68777777778), named as the western limit of the Cantabrian Sea, to the Breton Pointe Penmarc'h (48° N, 4° W47.7974444444-4.37486111111). The area enclosed by this line and the coast is about 223,000 km², and the greatest depth of water is 4735 m in Sables d'Olonne Canyon (46° N, 4° W45.9-4.05), north of the centre and 155 kilometres southwest of Île d'Yeu. With an average depth of 1774 metres, a water volume of 395,600 km³ is calculated. The main direction of wind and sea current is caused by the arrival of the Gulf Stream at the European mainland coast and leads from Pointe Penmarc'h at the southern coast of Brittany in a clockwise rotating current to Cabo Ortegal. The turbulences that occur between this current and the coast are considered quite dangerous in navigation, at least for small and medium-sized vessels.
Coast
On the Spanish Biscayan coast, which is mostly rocky but - especially in Asturias - interspersed with charming sandy bays with offshore rocky islands, lie from west to east the four autonomous regions of Galicia, Asturias, Cantabria and the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country, the Spanish part of the Basque Country. The northern coast of Galicia has a fjord-like character due to the Rías Altas. The economic centre of Asturias is the port city of Gijón. The capital of Cantabria, Santander, is also located on the Bay of Biscay and is touristy. In the Basque Country lies the province of Bizkaia, after which the bay is named. The port of the coastal town of San Sebastian is one of the largest in the country.
The French part of the coast belongs to the three regions of Nouvelle-Aquitaine (with the coastal towns of Bayonne, Bordeaux, Rochefort and La Rochelle), Pays de la Loire (with the coastal towns of Nantes and Saint-Nazaire) and Brittany (with the town of Lorient).
On the coast of Brittany, the Bay of Biscay meets the Celtic Sea at the Pointe de Penmarch, which is also the southern limit of the Baie d'Audierne.
Questions and Answers
Q: Where is the Bay of Biscay located?
A: The Bay of Biscay is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean south of the Celtic Sea. It is along the western coast of France from Brest south to the Spanish border, and the northern coast of Spain west to Cape Ortegal.
Q: What is the depth of the Bay of Biscay?
A: The average depth of the Bay of Biscay is 1,744 metres (5,722 ft), and the maximum depth is 2,789 metres (9,150 ft).
Q: Why is the Bay of Biscay named after the province of Biscay?
A: The Bay of Biscay is named after the province of Biscay, which is located in the Spanish Basque Country.
Q: What is the weather in the Bay of Biscay like?
A: The Bay of Biscay is home to some of the Atlantic Ocean's worst weather. Large storms occur in the bay, especially during the winter months.
Q: What is the history of ships in the Bay of Biscay?
A: Until recently, ships would be wrecked in Biscay storms, and many lives were lost.
Q: Have there been any improvements to prevent shipwrecks in the Bay of Biscay?
A: Improved ships and weather prediction have helped to reduce the problems of shipwrecks in the Bay of Biscay.
Q: What impact has improved shipping and weather prediction had on the Bay of Biscay?
A: Improved ships and weather prediction have helped to reduce the problems of shipwrecks in the Bay of Biscay.
Search within the encyclopedia