Sudan
![]()
The title of this article is ambiguous. For other meanings, see Sudan (disambiguation).
Template:Infobox State/Maintenance/TRANSCRIPTION
Template:Infobox State/Maintenance/NAME-German
The Republic of Sudan ([zuˈdaːn], also [ˈzuːdan], English Republic of the Sudan, Arabic جمهورية السودان, DMG Ǧumhūriyyat as-Sūdān) is a state in northeast Africa with access to the Red Sea. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the east, Ethiopia to the southeast, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, and Libya to the northwest. With an area of more than 1.8 million square kilometres, the country is about five times the size of Germany and the third largest country on the African continent. Of the 40 million inhabitants, more than a fifth live in the capital region around Khartoum, which forms a densely populated triangle with the cities of Omdurman and Bahri.
The Republic of Sudan has been independent from the United Kingdom (Anglo-Egyptian Sudan) since 1 January 1956. On 30 June 1989, Umar al-Bashir came to power in a military coup and ruled the country as president from then on using repressive means. On 11 April 2019, after 30 years in office, al-Bashir was arrested and deposed following another military coup and a state of emergency was declared. After a long struggle, the military leadership and the civilian opposition agreed on a transitional government.
South Sudan has been independent from Sudan since the referendum of 9 July 2011. Until the independence of South Sudan, Sudan was the largest African territorial state.
The official languages in Sudan are English and Arabic.
Country name
The country name is an abbreviation of the medieval Arabic term Bilād as-Sūdān, 'land of the blacks', which in this specific case meant the Christianized kingdoms in Nubia. Grammatically, the word is derived from the feminine form of aswad (Arabic أسود, DMG aswad 'black'). Sudan also refers to the savannah zone of West Africa south of the Sahara from the Atlantic coast to northern Nigeria; in the east, it includes parts of Chad and Darfur in Sudan and South Sudan.
"Sudan" has a masculine gender in German ('der Sudan', 'in Sudan'). The Standing Committee on Geographical Names does not provide for an article when using the short form of the country name. However, in Switzerland as well as in Austria, the short form of the country name with masculine gender and article is also officially used. In general usage, however, the use of the masculine in the nominative, dative and accusative is also common in Germany.
Geography
→ Main article: Geography of Sudan
Topography
Sudan is located in northeastern Africa. With an area of 1,861,484 km², the national territory covers slightly more than six percent of the continent. Among African states, only Algeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo are larger in area.
In total, Sudan has a national border of 6819 km in length. In the north, it borders Egypt for 1276 km, whereby the course of the border largely corresponds to the 22nd parallel north. Three areas deviate from this, the ownership of each of which is disputed: the Hala'ib Triangle, the Bir Tawil area, and the Wadi Halfa Salient. In the northeast, Sudan has 853 km of access to the Red Sea and thus a connection to the Indian Ocean.
Sudan borders Eritrea to the east (682 km), Ethiopia to the southeast (744 km), South Sudan to the south (2158 km), the Central African Republic to the southwest (174 km), Chad to the west (1403 km), and Libya to the northwest (382 km). On the southern border, the affiliation of the Abyei area is disputed between Sudan and South Sudan.
Relief
Its relief is determined by the basin landscape of the Nile and its peripheral mountains. Thus, in the northeast rises the mountainous region of Djibal al-Bahr al-ahmar on the Red Sea, which reaches an altitude of up to 2259m. The southwestern edge of the basin is formed by the North Equatorial Sill and the Central African Sill, which also form the watershed between the Nile and Congo systems. In the west, a basalt mountain range rises on the Marra Plateau, whose highest elevation of 3088 meters is Mount Marra, also the highest mountain in Sudan, and forms the geographical boundary with the Chad Basin. In the center rise the Nuba Mountains, which range in height from 500 meters to 1325 meters. In the north, the country merges into the Sahara on both sides of the Nile, the part west of the Nile being called the Libyan Desert and the part east of the Nile the Nubian Desert. In the region around Khartoum, where the White Nile and Blue Nile merge to form the Nile proper, wide, flat clay plains spread out.
Climate
High temperatures and summer rains, especially in the south, characterize Sudan's tropical climate. In the rainy season from April to November, rainfall is distributed from 1500 millimeters in the south to less than 100 millimeters in the north. The average monthly temperatures are between 24 degrees Celsius and 32 degrees Celsius. Due to the desert climate in the north, temperatures can reach 41 degrees Celsius during the day and 4 degrees Celsius at night.
Hydrology
From a hydrological perspective, Sudan is predominantly influenced by the Nile. Most of the East African country is located in its catchment area. However, the Nile in Sudan loses water primarily due to the desert climate. Irrigation field cultivation is practiced on the banks of the Nile. The flooding disaster in the summer of 2020 was caused by heavy rains on the upper reaches of the Blue Nile. Almost all river water comes from either equatorial Africa or Ethiopia. In addition, there are some coastal rivers, but most are dry due to high aridity. In the west of the country there are connections with the Chad Basin and other endorheic basins.
See also: List of rivers in Sudan
flora and fauna
The vegetation ranges from the sparsest plant growth in the northern deserts and semi-deserts to briar savannahs in the Sahel, dry savannah with tall grass, and wet savannahs. The forest cover decreased by 1.4 percent between 1990 and 2000. The diverse fauna includes elephants, buffaloes, giraffes, antelopes, hyenas, lions, hippos and crocodiles as well as numerous birds of prey and water birds, especially in the central Sudan.
National Parks
→ Main article: National parks in Sudan
Sudan has ten national parks (as of 2006). The system of protected areas also includes nature reserves and bird sanctuaries. The mountain Barkal with the historical city Sanam belong to the world heritage of the UNESCO and both together form the ancient capital Napata of the kingdom of Kush.
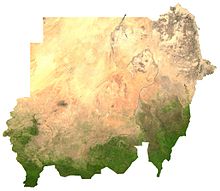
Satellite image of Sudan, showing the wetter south and the drier north.
Search within the encyclopedia