Spanish language
![]()
Spanish is a redirect to this article. For other meanings, see Spanish (disambiguation).
The Spanish or Castilian language (Spanish; proper name español [espaˈɲol] or castellano [kasteˈʎano]) belongs to the Romance branch of the Indo-European language family and, together with Aragonese, Asturleonic, Galician and Portuguese, forms the closer unit of Ibero-Romance. In a broader view, Spanish can also still be placed in Western Romance together with Catalan, French, Occitan and other smaller Romance languages such as Northern Italian.
The science that deals with the Spanish language and Spanish literature is called Hispanic studies. The Spanish language area is referred to as Hispanophony. Because of historical colonialism, Spanish is the most common native language on the American double continent and is considered a world language, for example, because of its function as the official language of numerous international organizations. (In Spain itself, however, Spanish is not the only language, see Languages in Spain). The Instituto Cervantes is entrusted with the maintenance of the Spanish language worldwide.
Spanish is written with Latin letters. In modern Spanish, the acute accent for vowels and the two characters ñ and ü are also used. In older dictionaries, the ch and ll can still be found as independent letters.

Andrés Bello

The Spanish language academy in Madrid, the Real Academia Española
.jpg)
Portrait of Antonio de Nebrija
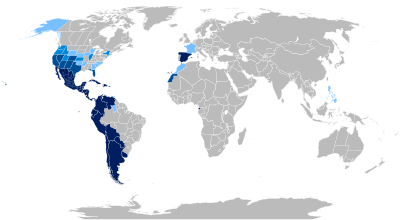
Spanish as a national language Unofficially, spoken by 25 % of the population Unofficially, spoken of 10-20% of the population. Unofficially, spoken of 5-9 % of the population Spanish-based creole languages
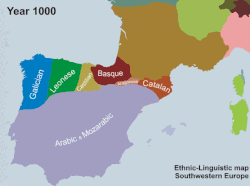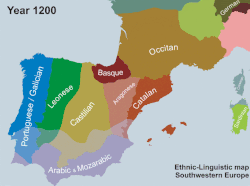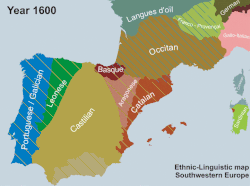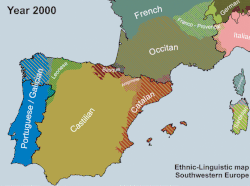
Linguistic development of southwestern Europe in the 2nd millennium AD. Chr.
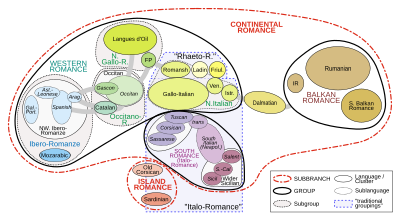
Relationships and affinities of the Romance languages (Romania)
Distribution
Spanish is currently (2017) spoken by around 440 million people as a native language and is thus the second most widely spoken native language after Chinese and the second most widely spoken world language after English in the narrower sense of its definition. Including second language speakers, the number of speakers (2017) amounts to 512 to 572 million Thus Spanish - after English, Mandarin and Hindi - occupies the fourth place of the most spoken languages in the world. Most Spanish speakers live in Mexico, the Caribbean, South and Central America, and Spain. The United States is home to about 58 million speakers (as of 2017), placing it second in the world after Mexico and ahead of Colombia and Spain. Although the language does not have official status in any state, the number of speakers is over 30% in some US states in the Southwest, such as New Mexico or California, but also in Texas. Spanish is spoken by a large proportion of the population in Belize (> 55% in 2010 compared to 46% in 2000), Morocco (just under 5% in 2017), Western Sahara, and Trinidad and Tobago. According to a 2015 study (Ethnologue 2015), Spanish is second only to Mandarin with 399 million native speakers. In Portuguese-speaking countries such as Portugal and Brazil, Spanish is often understood due to linguistic proximity, even if the Portuguese speakers do not speak the language themselves. Conversely, however, Portuguese is barely intelligible to Spanish speakers who do not speak the language because of its phonetic peculiarities. In linguistic contact zones in South America, mixed dialects have developed, some of which are called "Portuñol".
With more than 21 million learners, Spanish is also the second most studied foreign language in the world after English (together with French and Mandarin). Spanish serves as the supranational official or working language in the European Union, the African Union, the Organization of American States, the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, the Union of South American Nations, the Central American Integration System, and the United Nations.
Spelling
The spelling of Spanish pursues the ideal of reproducing the spoken word sound by sound. Thus, foreign words that are often adopted are adapted in their spelling in such a way that the pronunciation results automatically (examples: English bacon becomes Spanish beicon or English football becomes Spanish fútbol). In the case of Latin American variants, this only applies with restrictions (in some cases, letters are pronounced differently if the word is of Indian origin, especially ll and x).
See also: Spanish alphabet and hyphenation in the Spanish language
¿ and ¡
A special feature of the Spanish language is to introduce questions and exclamatory sentences with the ¿ (signo de interrogación) or the ¡ (signo de exclamación, sometimes also signo de admiración). This is usually only done in the Asturian and Galician languages. The question mark was introduced by the Real Academia Española in 1754 in the second edition of the orthography.
Examples
- El español es muy fácil, ¿verdad?
¡Por supuesto!
Spanish is very easy, right?
Absolutely!
- ¡Hola! ¿Cómo estás?
Bien, ¿y tú?
Hello! How are you?
I'm well, and you?
The inverted exclamation mark "¡" for the Spanish language is in ISO 8859-1 and Unicode at code 161 (U+00A1) and can be generated on any keyboard under Windows by Alt + 173 on the number pad or Alt + 0161. On a Macintosh, this is generated by Alt + 1/!, and on Linux/X11 by ⇧ + AltGr + 1/! An upside-down question mark "¿" can be entered as follows; under Windows with German layout by means of the key combination Alt+168, where the digits of the so-called numeric keypad must be used, or Alt+0191. On the Macintosh it is created by Alt + ß/?, under Linux by ⇧ + AltGr + ß/?.
.jpg)
Trilingual billboard in Barcelona (detail). The opening exclamation mark is only used in Spanish, not in the regional language (Catalan).
Questions and Answers
Q: What is the Spanish language called in Spanish?
A: The Spanish language is called "español" in Spanish.
Q: How is "español" pronounced in Spanish?
A: "Eh-span-yole" is the pronunciation of "español" in Spanish.
Q: What is another name for the Spanish language?
A: The Spanish language is also called Castilian.
Q: What kind of language is Spanish?
A: Spanish is a Romance language.
Q: Which Romance language is the most widely spoken in the world?
A: Spanish is the most spoken Romance language in the world.
Q: How many people in the world speak Spanish as their first language?
A: As of December 2021, over 489 million people around the world spoke Spanish as their first language.
Q: What is the IPA transcription for the word "español"?
A: The IPA transcription for the word "español" is /espaɲol/.
Search within the encyclopedia