Smartphone
Smartphone ([ˈsmaːɐ̯tfoʊ̯n]; [ˈsmɑɹtfoʊ̯n] AE, [ˈsmɑːtˌfəʊ̯n] BE) (English, roughly "smart phone") is the name given to a mobile phone (colloquially cell phone) with extensive computer functionalities and connectivity. The term serves to distinguish it from conventional ("pure") mobile phones. Early smartphone precursors in the late 1990s combined the functions of a personaldigital assistant (PDA) or organizer, with which one could manage contacts and one's calendar, for example, with the functionality of a pure mobile phone. Later, the functions of a portable media player, a digital and video camera, and a GPS navigation device were added to the compact device. Key features are touch screens for operation and computer-like operating systems. Internet access is optionally possible via mobile broadband connection of the mobile phone provider or WLAN.
The first mobile phones with smartphone functions already existed in the late 1990s. The term smartphone was first coined in 1999 by the Swedish company Ericsson. The introduction of the iPhone in 2007 by Apple led to an upheaval in the mobile phone market and smartphones gained significant market share. Today, most mobile phones sold are smartphones. With internet access permanently with them, this triggered a change in internet usage patterns, especially social networks such as Facebook, and enabled new forms of communication via services such as WhatsApp and Instagram. However, these possibilities of permanent use can also lead to smartphone addiction and change the social behaviour of users.
In the 2010s, Android, which is now used by almost all manufacturers, became the most widespread smartphone operating system, followed at some distance by Apple iOS, which is only used on Apple devices.
The smartphone has become the epitome of the digital lifestyle.
A smartphone shows the main page of the German-language Wikipedia in the mobile version.
Basics
Smartphones can be distinguished from traditional mobile phones, PDAs and electronic organizers by the following characteristics:
- In terms of design and operation, smartphones are not only optimized for making phone calls, but are also intended to enable the operation of a wide range of applications in a small space. Typical features are therefore relatively large and high-resolution screens, alphanumeric keyboards and/or touchscreens compared to older mobile phones.
- Smartphones usually have an operating system with an open API (see section Operating systems). It allows the user to install programs from third-party manufacturers. In contrast, mobile phones usually have a predefined program interface that can only be extended to a limited extent, e.g. by Java applications.
- Smartphones often have various sensors that are rarely found in classic mobile phones. These include, in particular, motion, photo (RGB and black and white), position, magnetic field, light, barometer and proximity sensors as well as GPS receivers.
- Individual models like the Samsung Galaxy S4 and Note 3 released in 2013 have ambient temperature and humidity sensors. So far, only the Samsung Galaxy Note 4 released in 2014 has a sensor for measuring ultraviolet radiation.
- The storage space of some mobile phones can be expanded using a microSD memory card. Advantages over cloud storage include location independence from cellular stations, zero latency, privacy, faster transfer speeds and no reduction in usage due to the cellular contract, as well as possible data recovery in the event of device failure and sparing of the write cycles of the non-replaceable internal memory board. In addition, the USB port is not occupied as with storage media connected via USB on-the-go accessories.
Through these features, smartphones offer the basics for mobile office and data communication in a single device. Users can enter data (such as addresses, texts and appointments) via the keypad or a stylus and install additional software themselves. Most devices have one or more digital cameras for capturing still and moving images and for video telephony.
The connection types used in PDAs, e.g. for synchronization, such as WLAN, Bluetooth, infrared or the USB cable connection, are supplemented by connection protocols previously used in mobile telephony, such as GSM, UMTS (and HSDPA), GPRS and HSCSD.
For example, in addition to mobile telephony, it is also possible to use SMS, MMS, e-mails and, with modern devices, video conferencing via UMTS or Internet telephony (VoIP) with WLAN via Internet access points while on the move. Theoretically - and to some extent also in practical use - in addition to audio and video streaming from the Internet (for example via WLAN), television programs can also be received via DVB-H and, with the appropriate hardware, DVB-T as well.
Another example is built-in or optional Java support (based on CLDC or MIDP) - mobile phones are considered one of the most popular applications of embedded Java.
Smartphones are also increasingly used for remote control of digital devices, such as cameras, action camcorders, AV receivers, TVs or quadcopters.
History
The first smartphone is considered to be the Simon, developed by BellSouth and IBM and marketed in part of the USA from mid-1994 to early 1995 as the "Personal Communicator". The forerunner of smartphone systems was the PEN/GEOS 3.0 from the manufacturer GeoWorks, which was used in the Nokia Communicator series introduced in 1996. When Nokia switched to a different processor for the 92x0, 9300, 9300i and 9500 Communicator series, the company formed an alliance with Psion and its EPOC system to develop the Symbian platform. Symbian was the most widely used smartphone operating system for a long time and had a market share of about 73% in 2006. The main competitors were Windows Mobile, Blackberry OS and Palm OS. The term smartphone was first coined in 1999 by the Swedish company Ericsson. Ericsson called the R380 model with touchscreen, Internet browser and calendar a smartphone when it was presented at the Cebit trade fair.
In 2006, the LG Prada appeared, model name "KE850". It is considered the first mobile phone with a capacitive touch screen, and is equipped with a 2-megapixel camera, 144p film resolution, LED lighting and miniature mirror for self-portraits. The storage space can be expanded by means of a MicroSD memory card.
The introduction of the iPhone by Apple with its multitouch user interface in 2007 marked a turning point in the smartphone market. New operating systems such as Android, Palm webOS and Windows Phone 7 could be operated mainly or exclusively via touchscreens. Symbian quickly lost ground as a result, and by the fall of 2011 was roughly on par with iOS. Between 2008 and 2011, all major manufacturers of Symbian devices announced that they would rely on other systems in the future.
The most frequently installed mobile operating system on smartphones is Android from Google. Since 2011, the sales figures of mobile devices with Android have been significantly higher than those with other operating systems, which is partly due to the significantly lower average selling price of mobile phones with Android. According to IDC, the market share in sales of Android devices in 2019 was 86.6%. Also with a significant market share after that is iOS from Apple (market share according to IDC in 2019: 13.4%). The Finnish manufacturer Nokia, which was the leading manufacturer of mobile phones for many years (1998 to 2011), offered its smartphones almost exclusively with Microsoft's Windows Phone operating system since 2012. In 2014, Nokia sold its mobile phone division to Microsoft.
Since 2009, the increasing importance of smartphones has led to numerous legal disputes over patents and design rights involving all major smartphone manufacturers. Launched in 2013, the Galaxy S4 is the world's first TCO-certified smartphone. At the end of 2013, the Fairphone was launched, the first smartphone in which fair trade and environmental aspects were to play a greater role.
Global smartphone sales have been declining since Q4 2017. For the full year (2017), a total of 1.472 billion smartphones were shipped worldwide, down less than 1% from the 1.473 billion units shipped in 2016. The highest market shares in the smartphone market are currently (as of 2020, sorted by market share) held by Samsung, BBK Electronics, Huawei, Xiaomi and Apple.
Since 2019, starting with the iPhone 11, manufacturers increasingly do without the inclusion of a plug-in power supply in the scope of delivery, with the reference to environmental protection. A similar intention is being pursued by the EU Parliament with the EU Radio Equipment Directive (RED). With this directive, the European Commission wants to adopt mandatory regulations for uniform charging sockets in order to minimise the electrical waste caused by different power supply units. However, to achieve the charging speed supported by the terminal device, the user may have to purchase a separate power supply with increased power. The additional packaging material when buying a new power supply worsens the carbon footprint.
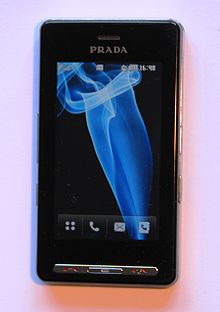
Home screen of the LG Prada, 2006

The Simon Personal Communicator from IBM from 1994
Questions and Answers
Q: What is a smartphone?
A: A smartphone is a mobile phone that can also be used as a computer. It is small enough to fit in the user's hand and has many features such as sending and receiving emails, text messages, photographs, multimedia messages, browsing the internet, playing games, video chat, mobile payment for goods or services, barcode scanning and more.
Q: How do smartphones work?
A: Smartphones work by running an operating system that is often common between devices to ensure compatibility. The majority of smartphones run on Apple iOS or Google Android but others use Windows Phone or BlackBerry OS. Most can do multitasking which helps the user do things quicker and easier. Additionally users can get more programs from app stores such as the Apple App Store and Google Play which can help them complete special tasks.
Q: What are data communication rates for smartphones?
A: Data communication rates vary depending on where they are located but most smart phones use 3G technology to make them fast enough to practically use internet and other data features with speeds estimated between 200kbit/s to 14Mbit/s (megabits per second). Faster 4G networks operate in many places with speeds estimated as fast as 100Mbit/s to 1Gbit/s (gigabit per second) while 5G was introduced in a few places in 2019.
Q: How are smartphones powered?
A: Smartphones are powered by batteries however over time the amount of energy they can store decreases causing them to become slower and later turn itself off without the user asking for it. Some smartphones are designed so that users can take off the rear cover and replace weakened batteries while newer models may not have this feature available.
Q: What type of functions does a smartphone have?
A: Smartphones have many functions including sending and receiving emails, text messages, photographs & multimedia messages; registering contacts; calculator & currency conversions; alarm functions; browsing the internet using a mobile browser; playing games; video chat; mobile payment for goods or services; barcode scanning; photography & video recording; using as torch to make light in dark areas; taking & searching notes; showing map of user's location by GPS (Global Positioning System); etc.
Q: Can older phones also use computer technology?
A: Yes, older phones also used computer technology but lacked many of parts of computers that were too big to fit into a phone whereas modern phone makers have been able to use smaller parts making them suitable for use with computers.
Search within the encyclopedia