Seattle
![]()
The title of this article is ambiguous. For other meanings, see Seattle (disambiguation).
Seattle (English: [![]()
![]() sɪˈætəl]; German: [siˈɛtl̩]) is the largest city in the northwestern United States. It is the administrative seat of King County in the U.S. state of Washington and is located between Puget Sound and Lake Washington, about 155 kilometres south of the border with Canada. Along with Vancouver and Portland, Seattle is the transportation hub and the economic, scientific and cultural center in the Pacific Northwest region.
sɪˈætəl]; German: [siˈɛtl̩]) is the largest city in the northwestern United States. It is the administrative seat of King County in the U.S. state of Washington and is located between Puget Sound and Lake Washington, about 155 kilometres south of the border with Canada. Along with Vancouver and Portland, Seattle is the transportation hub and the economic, scientific and cultural center in the Pacific Northwest region.
The city is nicknamed The Emerald City, which is a reference to the abundance of greenery around the city and the large forests (it is almost never referred to as such by locals, however), and Rain City - although rainfall is lower than in many other American cities. The nickname comes from the many cloudy and rainy days each year. It is also referred to as Jet City by locals, which is a reference to the nearby Boeing plants.
The Port of Seattle is a major commercial hub for trade with Asia, Alaska and Hawaii. The most important resident industries are aerospace (Boeing), iron and steel industry and wood processing. Seattle's architectural landmark is the Space Needle tower, built for the 1962 World's Fair. The city is home to the University of Washington.
The town was named for Noah Sealth, chief of the Duwamish and Suquamish, better known as Chief Seattle.
Geography

enlarge and show information about the picture
![]()
360° panorama of Seattle, photographed from the Space Needle
Geographical position
Seattle is located on the isthmus between Puget Sound and Lake Washington at 47°37'35" N. B. and 122°19'59" w. L., in the shadow of the Olympic Mountains to the west; the Issaquah Alps and the Cascade range join it to the east. The rivers, lakes, and forests were once very fertile, so that the original inhabitants formed one of the few settled hunter-gatherer cultures.
The city itself is very hilly, with the steepest grades being in Old Town. The geography of the Downtown district has been greatly altered over the decades. Whereas at the beginning of settlement it was a short, flat, and washed-over coastline followed by a bluff, the bluff was flattened and, in order to end the regular flooding, the land on the coast was filled in, so that today one finds a continuous steep rise from the coast in the Downtown district. This work created a network of underground passageways and basements, Seattle Underground.
Seattle is dominated by water, along with mountains and hills. On the western side, Puget Sound allows access to the Pacific Ocean. Within the city are several lakes, such as Lake Washington and Lake Union, which are connected by canals. The city has an area of 369.2 km2. 217.2 km2 of it is land, 152.0 km2 is water. Thus, the share of water in the area is 41.16%.
Due to its location, the city and its surroundings allow a wide range of leisure activities from water sports to hiking and mountaineering to winter sports.
Seattle is located in the Pacific Northwest on a geologically active zone. Several strong earthquakes have shaken the city in its history so far:
- 14 December 1872 (Mw 7.3)
- 13 April 1949 (Mw 7,1)
- 29 April 1965 (Mw 6.5)
- 28 February 2001 (Mw 6,8)
Just 83 kilometres to the southeast is Mount Rainier, a 4,392-metre-high stratovolcano that last erupted in 1854.
Climate
| Seattle, Washington | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monthly average temperatures and precipitation for Seattle, Washington
Source: National Weather Service, US Dept of Commerce | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The climate is maritime. There are (September to early June) both humid (humides) and dry (arides) climate (late June to late August). The average annual temperature is 11.2 °C. The frequent rainfall results in an annual total of 857 mm. In summer there is almost no rainfall, while in winter there is up to 140 mm of precipitation per month. Temperatures are mild, which is a typical sign of maritime climate. The lowest average temperatures are around 7 °C, while in summer they reach just under the 20 °C mark between June and September. The surrounding mountains protect the city from strong gusts of wind. In winter there is only light snowfall.
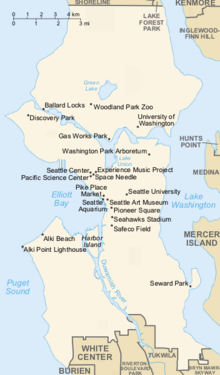
Map of Seattle
History
The arrival of the Denny family, known as the Denny Party, who landed at Alki Point on November 13, 1851, is considered the birth of Seattle. They relocated to the more sheltered Elliott Bay, now Pioneer Square, in April 1852. The first plans for the establishment of a settlement (Town), known as plats, were filed on May 23, 1853. The corresponding first cadastral boundaries can still be seen in the cityscape today. The town's first boom was based on the lumber industry and the money extracted from the pockets of loggers by enterprising ladies like Mother Damnable, among others. The Seattle municipality has gone through several boom-crash cycles and successfully used times of crisis to expand its infrastructure.
The founding of the city (City) as such dates to 1869, and the naming after the Native American chief Seattle was largely the result of the efforts of David Swinson "Doc" Maynards, the city's first physician.
Between 1890 and 1910, Seattle's population increased sixfold. On June 6, 1889, a major fire destroyed much of the city. A dry spring and high winds hampered the fight against the flames. By evening, nearly 26 acres of the city had been destroyed. In 1909, the Alaska-Yukon-Pacific Exposition was held on what is now the University of Washington campus. In 1914, one of Seattle's first landmarks, the Smith Tower, opened. At 159 meters, it was the tallest building west of the Mississippi River at the time. In 1919, Seattle was the site of the country's first general strike.
The beginning of modern Seattle is seen as the 1962 Century 21 Exposition, which saw the construction of many of the city's landmarks such as the Space Needle, KeyArena (Coliseum), Pacific Science Center, and Seattle Center Monorail. In 1994, similar to Portland, a new Urban Villages Strategy was adopted as part of the city planning process. It defined the districts intended for further concentration and intensification of trade and industry or as residential areas, the design of infrastructural investments, and the preservation of the cityscape and landscape and nature conservation.
In December 1999, on the fringes of the WTO conference in Seattle, violent clashes broke out between opponents of globalisation and the police.

Puget Sound News Company building, which was part of the American News Company, circa 1900.
Search within the encyclopedia