Rwanda
Template:Infobox State/Maintenance/NAME-German
Rwanda or Rwanda [ˈʁu̯anda] (Kinyarwanda u Rwanda, French le Rwanda [lə ʁwɑ̃ˈda]) is a densely populated landlocked country in East Africa. It borders Burundi, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda, and Tanzania. Because of its hilly landscape, Rwanda is also called the "land of a thousand hills". The main African watershed between the catchment areas of the Nile and the Congo runs through the national territory. From 1884 to 1916 Rwanda was a German colony as part of German East Africa. After World War I, it became a Belgian League of Nations mandate in 1919 and a UN trust territory after 1945. It became independent in 1962.
Due to structural problems, a high population density and conflicts between the Hutu and Tutsi ethnic groups - which culminated in the genocide of the Tutsi in 1994, in the course of which some 800,000 ethnic Tutsi and moderate Hutu were murdered by radical Hutu - the country was among the poorest in Africa. Since the end of the civil war, an economic reconstruction process has begun that has been favoured, among other things, by the exploitation of raw materials in the eastern Congo provinces. Since 2000, Paul Kagame has been in office as president, governing the country authoritatively in a kind of education and development dictatorship. The system of government is internationally criticized for lack of freedom of the press, suppression of the opposition, manipulation of elections and destabilization of eastern Congo.
With an average annual economic growth rate of about 8 percent in the period 2001 to 2015, Rwanda has long been one of the countries in Africa with the strongest economic growth. Large parts of the economy are controlled by the ruling Rwandan Patriotic Front party. Rwandan society is also characterized by the unusually high participation of women in economic and political power by African standards.
Etymology
The name Rwanda is derived from the Old Rwandan verb kwanda (to enlarge, to expand). Just as the prefix ku- (ku-anda = kwanda) characterizes a verb, in country names, for example, the syllables -Bu- or -Ru- as well as the article u- are prefixed to the root word.
root -anda: u-Ru-anda = uRwanda or u Rwanda (the growing country, Rwanda)
root -dage: u-Bu-dage = uBudage or u Budage (Germany, -dage from German)
root -faransa: u-Bu-faransa = uBufaransa or u Bufaransa (France, -faransa from France)
The country is spelled Rwanda in German, Rwanda in French (more rarely Rwanda).
Administration breakdown
See also: Administrative divisions of Rwanda
Since 1 January 2006, Rwanda has been divided into five provinces:
| Province | Capital | Area in km² | Population2012 | Inhabitants jekm² |
| Kigali | Kigali | 730 | 1.132.686 | 1.552 |
| North | Byumba | 3.436 | 1.726.370 | 502 |
| East | Rwamagana | 9.813 | 2.595.703 | 265 |
| South | Nyanza | 6.118 | 2.589.975 | 423 |
| West | Kibuye | 6.233 | 2.471.239 | 396 |
Previously, Rwanda was divided into the following twelve provinces: Butare, Byumba, Cyangugu, Gikongoro, Gisenyi, Gitarama, Kibungo, Kibuye, Kigali, Kigali Rural, Ruhengeri and Umutara. The five present provinces are further subdivided into a total of thirty districts.
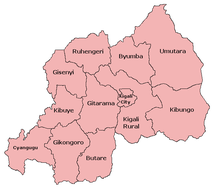
Administrative structure until 2005
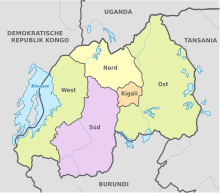
Current administrative structure
Questions and Answers
Q: Where is Rwanda located?
A: Rwanda is located in Africa.
Q: What are the neighboring countries of Rwanda?
A: The neighboring countries of Rwanda are Burundi, Congo-Kinshasa, Uganda, and Tanzania.
Q: What happened in the Rwandan genocide of 1994?
A: Over one million (1,000,000) people were killed in the Rwandan genocide of 1994.
Q: When did the Rwandan genocide occur?
A: The Rwandan genocide occurred in 1994.
Q: How many people were killed in the Rwandan genocide?
A: Over one million (1,000,000) people were killed in the Rwandan genocide.
Q: What is the significance of the Rwandan genocide?
A: The Rwandan genocide is significant because it was a systematic massacre of the Tutsi ethnic group by the Hutu majority, and it resulted in the deaths of a large number of people in a short period of time.
Q: What is the current status of Rwanda?
A: The current status of Rwanda is a developing country that is working towards rebuilding after the genocide, with a focus on economic development and reconciliation.
Search within the encyclopedia