Rhine
![]()
The title of this article is ambiguous. For other meanings, see Rhine (disambiguation).
The Rhine (Latin Rhenus; French Rhin, Italian Reno, Rhaeto-Romanic ![]() , Dutch Rijn, Alemannic Ry, Ripuarian Rhing) is a 1,232.7 km long river in Western and Central Europe and one of the busiest waterways in the world.
, Dutch Rijn, Alemannic Ry, Ripuarian Rhing) is a 1,232.7 km long river in Western and Central Europe and one of the busiest waterways in the world.
The headwaters of the Rhine lie mainly in the Swiss canton of Graubünden, its estuary arms reach the North Sea in the Netherlands, where it is the most water-rich tributary. From the confluence of the two main headwaters Vorderrhein and Hinterrhein, the river is usually divided into the following main sections: Alpenrhein, Hochrhein, including the Seerhein through Lake Constance, Oberrhein, Mittelrhein and Niederrhein, including the three estuary arms of the Deltarhein, Waal, Lek and IJssel.
The largest tributaries of the Rhine, measured by length, catchment area and mean discharge (MQ), are, ordered from source to mouth: Aare, Neckar, Main, Moselle and Meuse. With them, its catchment area shares nine states. The largest part of it in area is in Germany, followed by Switzerland, France, Austria and the Netherlands. The Rhine is the tenth longest river in Europe and the seventh longest to flow directly into the sea. Among the rivers of the German-speaking area, it is the second longest after the Danube and before the Elbe.
Basic data
The Rhine has a total length of 1,232.7 km. Of this, 376 km are in Switzerland (of which a large part of the 170 km long Hochrhein including Untersee is on the border with Germany), 695.5 km are in Germany (of which 182 km are on the border with France; if one adds the Hochrhein including Untersee, one gets 865.5 km for Germany) and 161.2 km are in the Netherlands. 883 km are usable for large-scale navigation. The average discharge just before the branching of the estuary arms is about 2300 m³/s. The highest discharge ever measured there was 12,000 m³/s (1926), the lowest 600 m³/s (1947). The river system as a whole delivers an average of around 2900 m³/s to the North Sea. The catchment area of the Rhine covers 218,300 km² (without the Meuse: 185,300 km²). † The administratively defined river basin district Rhine, which also includes adjacent parts of the coast and the coastal North Sea, is given with 198,735 km² (the Meuse basin is a separate river basin district). The water body index of the Rhine in Germany is 2. The Rhine is - with the Meuse - the largest river northwest of the main European watershed.
† For comparison, Volga 1,360,000 km², Danube 795,686 km², Dnepr 531,817 km², Don 425,600 km², Vistula 194,424 km², Elbe 148,268 km².
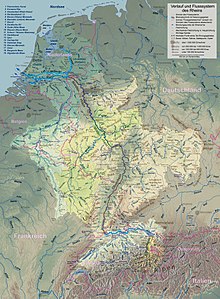
catchment area of the Rhine
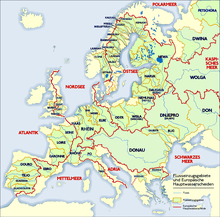
Map of European catchment areas
Etymology
The name "Rhine" possibly goes back to the Indo-Germanic word root H1reiH- for "flow". This root also gave rise to the German verb rinnen, the Ancient Greek verb ῥέω rhéō, German 'fließen', the Latin rivus (river) - which then gave rise to Spanish río and English river. The Celts called the river Rhenos, the Romans Rhenus. In antiquity, the river was also worshipped as Rhenus Pater ('Father Rhine'). It is possible that the name was first used by the pre-Roman population in the headwaters of the Rhine and then adopted by the Celts and Romans. However, the name could also have been introduced by the Celts themselves.
The name of the Rhine in the Romance and Germanic language forms of its catchment area is: Rhaeto-Romanic Rein, Italian Reno, Alemannic Rhy, French Rhin, Vorderpfälzisch Rhoi, südpfälzisch Rhei, lëtzebuergesch (Luxembourgish) Rhäin, ripuarisch Rhing, Dutch Rijn, Frisian Ryn.
In the headwaters, numerous larger and smaller headwaters contain the name part Rhine or equivalents in various Grisons Romance idioms such as Rein or Ragn. Examples:
- Vorderrhein area: Vorderrhein/Rein Anteriur, Rein da Medel (ital. Froda/Reno di Medel), Rein da Tuma, Rein da Curnera, Rein da Maighels, Rein da Cristallina, Rein da Nalps, Rein da Plattas, Rein da Sumvitg, Rein da Vigliuts, Valser Rhine
- Hinterrhein area: Hinterrhein/Rein Posteriur, Reno di Lei (Ital. ), Madrischer Rhein, Averser Rhein, Jufer Rhein. In the Dischma near Davos names such as Am Rin (place), Riner Tälli or Rinerhorn can be found.
The Rhine itself gives its name to the chemical element rhenium, which was discovered in 1925.
Search within the encyclopedia