Public transport
This is the sighted version that was marked on November 16, 2020. There are 2 pending changes that still need to be sighted.
![]()
This article or subsequent section is not sufficiently supported by evidence (for example, itemizations). Information without sufficient evidence may be removed soon. Please help Wikipedia by researching the information and adding good supporting evidence.
![]()
This article or paragraph presents the situation in Germany. Help describe the situation in other countries.
Public transport (PT) refers to that part of the transport of people, goods or messages that is accessible to every user in an economy or in the population, in particular the services of public goods transport, public passenger transport (public passenger transport) and services of publicly accessible postal and telecommunications services.
The characteristics of public transport are:
- general accessibility for every user (in the case of vehicle traffic, compulsory transport),
- Execution by special concessionary transport companies (for example, in the case of railroads, aviation, cableways, shipping, elevator systems) or on concessionary lines or routes or by concessionary service providers
- and, in the case of vehicle transport, the fixing of transport conditions or regulations and prices in published legal norms (timetable and tariff obligations).
A distinction is made between public transport
- as part of basic services or services of general interest with subsidized or appropriate tariffs
- Means of road, rail and ferry transport, the former actually being referred to in common parlance as "public transport", in Austria colloquially also as "Öffis". In this context, it becomes apparent that language usage and definition differ in meaning.
- Traffic with line carriers (for example, water supply, sewerage, telephone)
- wireless messaging (for example, public broadcasting)
- outside the basic service, without subsidized tariffs, but according to the concessions also with tariff and transport obligation and mostly in regular service (for example winter sports cableways, inland navigation, aviation)
Access and the object of transport are two different dimensions here. In terms of access, public and non-public transport (military installations and transport, private transport or individual transport ("IV"), private commercial transport and occasional transport) are opposed to each other. Both types of traffic can serve to transport people and/or goods.
In many countries, a distinction is made between long-distance and local (also regional) traffic, and there are also the terms domestic traffic and international traffic. In the case of the latter, there is a further division that designates traffic from one neighboring country through another as transit traffic. Smaller countries, for example, do not make any distinction between long-distance and short-distance rail services; in this case, there are only domestic trains and international trains. In Germany today, a very sharp organizational distinction is made between local public transport (ÖPNV) and long-distance passenger transport. In contrast, the GDR only knew local, domestic, transit and international transport.
There are the designations public long-distance and short-distance freight transport as well as public international and transit freight transport and equivalent designations for the corresponding passenger transport.
Public transport operators can be public or (partially) private transport companies. They can be particularly specialized for their transport tasks with regard to different transport sectors, including as special providers for long-distance, local or international services.
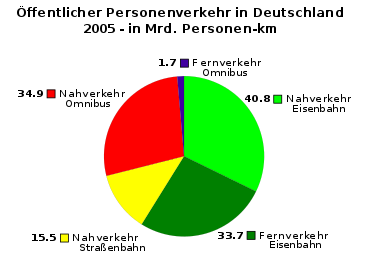
Transport performance of public transport (passenger transport) in Germany - according to figures from the Statist. Bundesamt
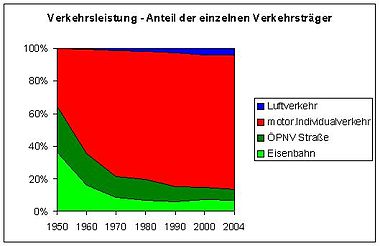
Transport performance of the various modes of transport (passenger transport) in Germany - in % - Source: Federal Environment Agency
See also
- Ticket
- Traffic Engineering
- Transport Ecology
- Mode of transport
- Transportation Sciences
- German Railways, Austrian Federal Railways, Swiss Federal Railways
Search within the encyclopedia