Pollutant
![]()
This article or section needs revision. More details should be given on the discussion page. Please help improve it, and then remove this tag.
![]()
This article or subsequent section is not sufficiently supported by evidence (e.g., anecdotal evidence). Information without sufficient evidence may be removed in the near future. Please help Wikipedia by researching the information and adding good supporting evidence.
In everyday language, pollutants are substances or mixtures of substances present in the environment that can be harmful to humans, animals, plants or other organisms as well as entire ecosystems. The damage can be caused by uptake by organisms or input into an ecosystem or its biomass. Harmful" is defined in a narrower sense as a substance because of its effect on an ecosystem (from microorganisms to plants, animals and humans).
However, this definition also shows the difficulty in defining this term. A specific, chemically defined substance (substance) cannot always be clearly assigned to or excluded from the category of pollutant (or also toxicant); rather, the quantity and the environmental situation also play a role. The effect of a pollutant (as well as a toxic substance) on an ecosystem may therefore have to be investigated and documented by field tests, long-term experiments and pollutant analyses in the form of qualitative detection reactions and quantitative instrumental measurements.
Natural and artificial pollutants
Among pollutants, a distinction is made between two groups in principle:
- natural pollutants - such as rock dust or mycotoxins (fungal toxins) - and
- man-made pollutants - of anthropogenic origin, i.e. caused or released by humans.
Both groups can have chemically different substances, organic or inorganic, but also strong structural differences and are composed of particles of different sizes.
Therefore, pollutants are also subdivided according to other aspects:
- Pollutants from agriculture
- Pollutants due to environmental pollution
- Pollutants due to improper storage, preparation and disposal
- Pollutants of natural origin
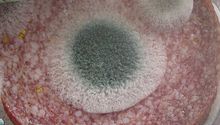
Salami with harmful mould

Bread with harmful mould
Pollutants from agriculture and horticulture
Possible pollutants here would be:
- Pesticides such as DDT or hexachlorobenzene (HCB) are used by farmers for pest control and can have harmful effects, especially if they are washed into groundwater or surface waters, as they are toxic, fruit-damaging, carcinogenic or mutagenic to many organisms and often very persistent.
- Nitrogen fertilization (for example with liquid manure) can, among other things, introduce nitrates into the groundwater or into foodstuffs. These nitrates are metabolized in the body to nitrites and can impair oxygen transport (methemoglobinemia); cyanosis can occur in infants. In addition, nitrite and proteins can form nitrosamines, most of which are classified as carcinogenic.
- Many mineral fertilizers contain phosphate fertilizers, which have a natural content of uranium and cadmium. These pollutants can accumulate in the soil and also enter the groundwater.

Slurry application from a slurry tank on grassland close to the ground
Search within the encyclopedia