Physical therapy
![]()
This article or section needs revision. More details should be given on the discussion page. Please help improve it, and then remove this tag.
Physiotherapy (ancient Greek φύσις phýsis, German 'nature', 'body' and θεραπεία therapeía, German 'serving', 'care', 'healing', thus roughly 'the restoration of natural function'), formerly also physiotherapy, is a form of specific training and the external application of remedies, with which above all the movement and functional capacity of the human body is to be restored, improved or maintained.
The treatments are carried out by physiotherapists and, in some areas, by masseurs and medical bath attendants. Physiotherapist is not an independent medical profession in Germany, but belongs to the health professions (formerly auxiliary health professions). The medical necessity of a treatment is exclusively determined by physicians and prescribed on prescription, except for preventive measures. Sports therapists, scientists and teachers do not meet the licensing requirements as physiotherapists and are not allowed to provide or bill physiotherapeutic remedies such as physiotherapy.

Physiotherapists working on patients with balance disorders and orthopaedic problems. Also shown in the picture: Assessment and testing of muscle function and stiffness, joint mobility, balance testing and gait assessment.

Physiotherapy training
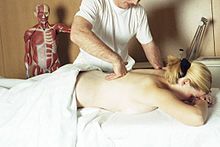
Treatment by a physiotherapist
Target
Physiotherapy bases its treatment on the patient's complaints and functional, movement or activity restrictions that are identified during the physiotherapeutic examination. It uses diagnostic and clinical reasoning based as well as educational and manual skills of the therapist. If necessary, it is supplemented by natural physical stimuli (e.g. heat, cold, pressure, radiation, electricity) and promotes the patient's own activity (coordinated movement as well as conscious perception). The treatment is adapted to the anatomical and physiological, motivational and cognitive conditions of the patient. On the one hand, the treatment aims at natural, physiological reactions of the organism (e.g. motor learning, muscle development and metabolic stimulation), on the other hand at an improved understanding of the functioning of the organism (dysfunctions/resources) and at self-responsible handling of one's own body. The goal is the restoration, maintenance or promotion of health and very often freedom from pain or pain reduction.
Research
In the English-speaking world, pathokinesiology/kinesiopathology, among other things, is seen as a characteristic science, which plays a central role for the professional identity of physical therapy and its differentiation from other professions, which, in contrast to it, do not deal professionally with the human movement system. Publications by research-based physiotherapists are published internationally in medical and scientific journals and are subject to peer review.
The work of a US-American research group, for example, has concrete applications in the establishment of specific diagnostic categories for the purpose of cause-related and targeted therapy of pain syndromes of the human locomotor system.
Search within the encyclopedia