Persian language
![]()
Persian is a redirect to this article. For other meanings, see Persian (disambiguation).
![]()
This article or section is still missing the following important information:
Phonetics and phonology
Help Wikipedia by researching and adding them.
The Persian language (Persian زبان فارسی, DMG zabān-e fārsī) is a pluricentric language in Central and Southwest Asia. It belongs to the Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family and is the official language of Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan. Persian is a major language in West and Central Asia and is spoken by 60 to 70 million people as a native language and by another 50 million as a second language.
In Persian, the language is called Fārsi (فارسی). Fārsī-yi Darī (فارسى درى) is the official modern name in Afghanistan ("Afghan Persian"), though Iranian Zarathustrians also call their language Darī. Tajik, written in Cyrillic, is the variety of Persian spoken in Central Asia, and Tat a variety in Azerbaijan and Dagestan (Russia).
New Persian, strongly influenced by Arabic, especially through the formation of loan words, developed in the Middle Ages into the most important scholarly and literary language of the eastern Islamic world and had a great influence on the neighboring Turkic languages (especially Azerbaijani, Ottoman, Turkic, and Chagataic), Armenian Georgian, and the languages of northern India, especially Urdu. For centuries, Persian was the higher official and educational language in the Mughal Empire in India and other Islamic-ruled states of the Indian subcontinent.
Many Persian words were also adopted into European languages. In German, we know the words "bazaar", "caravan", "magician", "paradise", "pistachio", "chess", "scarf" and "cheque", among others. Persian literature has become internationally known with poets such as Rumi, Omar Chayyām, Hafis, Saadi, Nezami, Jami, Ferdousi and Sadegh Hedayat.
Distribution
Persian is spoken by 60 to 70 million people as a native language and by another 50 million as a second language. About 41 million native speakers live in Iran, another 15 million in Afghanistan, and 15 million in Central Asia (mainly in Tajikistan and in Uzbekistan). Persian was used as an official language in parts of India from the 13th to the 18th centuries and was the only non-European language reported by Marco Polo to have been used in the court of Kublai Khan (13th century). Today, there are significant Persian-speaking communities in Iraq and the Gulf states (notably Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, and Kuwait). Other small language islands exist in Georgia, Azerbaijan, Russia, and the Pamir Mountains, among other places. Persian-speaking communities have also developed in Europe and the USA.
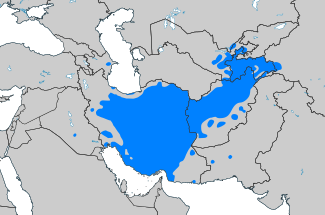
Present-day distribution of Persian in the Middle East. From the map it is clear that not all residents of Iran are native speakers of Persian and, on the other hand, Persian is the mother tongue for a large part of the population of Afghanistan and Tajikistan.
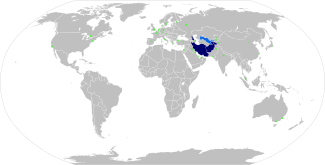
The Persian language in the world Blue : official language (Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan) Green : Persian-speaking minorities
Designations
Traditionally, this language is called Persian in European countries - named after the ancient Persian core province of Fārs (Pārs) in southern Iran.
Designations in Persian:
- In the Sassanid period the name of the language was Pārsīk or Pārsīg.
- Since about the time of the Arab-Islamic conquest of Persia, the name has been Fārsī (فارسی).
- For the New Persian written language, the term Fārsī-e Darī (فارسی دری) also appeared. The short form Dari (درى) is derived from Fārsī-ye Darbārī, "Persian of the royal court" (Persian دربار Darbār, 'royal court') and is in use in Afghanistan today.
- The Neo-Persian dialects of Central Asia have been called the Tajik language since the Soviet era.
Questions and Answers
Q: What is Persian?
A: Persian is a Western Iranian language, also called Farsi.
Q: What countries is Persian the official language of?
A: Persian is the official language of Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan.
Q: In what other countries is Persian spoken?
A: Persian is also spoken by many people in Pakistan, Uzbekistan, Azerbaijan, and by immigrants from Central Asia in Russia.
Q: Was Persian taught as a second language in schools in Pakistan?
A: Yes, Persian was taught as a second language in schools in Pakistan until 2006.
Q: What are the different names for Persian in different countries?
A: Persian is officially called Farsi in Iran, Dari and Farsi in Afghanistan, and Tajiki in Tajikistan.
Q: Are there many dialects of Persian?
A: Yes, Persian has many dialects.
Q: What foreign languages have influenced Persian?
A: Persian has words from French in Iran and many from Russian in Tajikistan.
Search within the encyclopedia