Paper
![]()
This article is about the material. Other meanings under Paper (disambiguation).
Paper (from Latin papyrus, from Ancient Greek πάπυρος pápyros 'papyrus shrub') is a sheet material consisting essentially of fibres of vegetable origin, formed by dewatering a fibre suspension on a screen. The resulting fibrous web is compacted and dried.
Paper is made from fibrous materials, which today are mainly obtained from the raw material wood. The most important fibrous materials are pulp, mechanical pulp and waste paper pulp. Waste paper recycled through paper recycling is now the most important source of raw material in Europe. In addition to the pulp or a mixture of pulps, paper often contains fillers and other additives.
There are around 3000 types of paper, which can be divided into four main groups according to their intended use: graphic papers (printing and writing papers), packaging papers and board, hygiene papers (e.g. toilet paper, paper handkerchiefs) and the wide range of technical and special papers (e.g. filter papers, cigarette paper, banknote paper).

stack of sheets
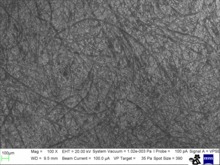
Paper sheet enlarged a hundred times

Waste paper

Historical hemp paper
Delimitation
Paper, cardboard, paperboard
Paper, cardboard and paperboard are distinguished on the basis of their mass per unit area, among other things. DIN 6730 avoids the term cardboard and only differentiates between paper and cardboard on the basis of the limit value 225 g/m² (mass occupancy). Colloquially, however, cardboard is a common term for a material in the range 150 g/m² to 600 g/m², which is typically thicker and stiffer than paper. In the allocation to mass per unit area, there are overlap ranges between paper and board and between board and cardboard:
| Designation | grammage |
| DIN 6730 | |
| Paper | 7 g/m² to 225 g/m² |
| Cardboard | from 225 g/m² |
| Colloquial (German) | |
| Paper | 7 g/m² to 225 g/m² |
| Cardboard | 150 g/m² to 600 g/m² |
| Cardboard | from 225 g/m² |
In some cases, in the case of the colloquial three-way division into paper, cardboard and paperboard, other limit values are given for the overlap ranges, for example:
| Designation | grammage |
| Paper | 7 g/m² to 250 g/m² |
| Cardboard | 150 g/m² to 600 g/m² |
| Cardboard | from 500 g/m² |
The minimum grammage of paperboard is stated differently depending on the source, for example as 220 g/m² or 600 g/m². The fluid weight limits are also based on innovations in production technology. The basis weight should therefore be regarded today as an approximate guide and as one of several distinguishing criteria.
Pseudo papers
Pseudo-papers (paper-like) such as papyrus, tapa, amatl and huun - all of plant origin - differ from paper mainly in the technique of production: plant fibres are joined together by tapping and formed into a sheet. In the production of real paper, the fibers are soaked in water and separated from each other. Then the fibers must be placed as a thin layer on a screen, dewatered and dried. The intertwined, matted fibres form the paper.
Paper Market
→ Main article: Paper industry
Worldwide, 406 million tons (as of 2014) of paper, cardboard and paperboard are produced annually. The largest producers (as of 2014) are China (108 million tonnes), the USA (73 million tonnes), Japan (26 million tonnes) and Germany (22.5 million tonnes).
The European paper industry accounts for one third of the world's paper production capacity. Europe is the leader in the production of printing and writing paper, followed by Asia and North America, and accounts for almost 26% of total paper and board production. Consolidation of the European paper industry over the last decade has reduced the number of companies, paper mills and paper machines in Europe, but at the same time significantly increased production capacity. It is estimated that the 20 largest paper producers currently account for almost 40% of global paper and board production. The turnover of the European paper industry was around 79 billion euros in 2015. 180,000 people work in the European pulp and paper industry. In addition to large paper manufacturers such as UPM-Kymmene, Stora Enso, International Paper, Svenska Cellulosa Aktiebolaget (SCA), Metsä Board, Sappi or the Smurfit Kappa Group, there are a large number of medium-sized and smaller paper manufacturers such as Papierfabrik Palm or Kartonfabrik WEIG.
The German paper industry, whose interests are represented by the Verband Deutscher Papierfabriken (VDP), is number one in Europe with a production volume of 22.6 million tonnes (2015) of paper, board and cardboard and ranks fourth worldwide behind China, the USA and Japan. The German pulp and paper industry's approximately 40,600 employees generate sales of 14.4 billion euros (2015) in 162 mills, an increase of 0.9% over the previous year.
Questions and Answers
Q: What is paper made of?
A: Paper is mostly made of wood fibers that are pressed together.
Q: How do people write on paper?
A: People use pencils or pens to write on paper.
Q: What are books made of?
A: Books are made of paper.
Q: Can paper absorb liquids?
A: Yes, paper can absorb liquids such as water.
Q: Are there different types of paper?
A: Yes, there are many different types of paper.
Q: What is the pulp and paper industry?
A: The pulp and paper industry is a group of companies that use wood as a raw material to produce pulp, paper, board, and other cellulose-based products.
Q: What can people do with paper?
A: People can write on paper, make books, and use it to clean things due to its absorbent properties.
Search within the encyclopedia