Normal force
![]()
This article deals with a force acting perpendicularly on a surface. For the cutting reaction see there.
A normal force is an interaction force in the contact zone between two bodies or a cutting force in a rod-shaped component. It is perpendicular to the contact surface or cut surface. The normal force acting in the direction of the normal vector generates compressive or tensile stresses. The normal force determines, among other things, the frictional force between two bodies.
In the example, the formula for calculating the normal force 

In it, the angle of the inclined plane α 



In addition to the case of a pure load due to the weight, normal forces also occur, for example, as a result of aerodynamic downforce or due to the cornering pressure when negotiating a banked curve. In the latter case, the normal force results in:
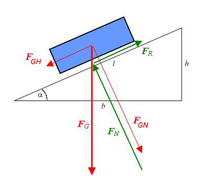
Inclined plane: FN is perpendicular to the supporting surface and acts on the block
Beam Theory
→ Main article: Beam theory
In 1st order bar theory, the normal force is the longitudinal force parallel to the bar axis direction:
Questions and Answers
Q: What is normal force?
A: Normal force is the force that the ground (or any surface) pushes back up with.
Q: What would happen if there was no normal force?
A: If there was no normal force, you would slowly seep into the ground.
Q: How is the normal force on an object related to its weight?
A: On a flat surface, the normal force of an object is equal to its weight (the object's mass multiplied by the force of gravity).
Q: How does an inclined plane affect the normal force?
A: On an inclined plane, the normal force is reduced by the angle, and it can be calculated using m g c o s θ.
Q: What does θ represent in this equation?
A: θ represents the angle of inclination in this equation.
Q: When would cosθ be 1?
A: cosθ would be 1 when θ (angle)is 0, which occurs on a flat surface.
Q: How do these two equations compare to each other? A: The two equations are equal when on a flat surface.
Search within the encyclopedia

