Nasal cavity
The paired nasal cavity (cavitas nasi) is part of the respiratory tract and contains the olfactory organ. The nasal septum (Septum nasi) separates the left and right nasal cavities, in each of which an anterior nasal cavity (Vestibulum nasi) located within the outer nose and the actual nasal cavity (Cavum nasi proprium) located lower down can be distinguished. The cavum nasi, which is lined with a mucous membrane with ciliated epithelium, is subdivided into the nasal passages (meatus nasi) between the floor and roof of the nasal cavity by bony nasal conchae (conchae nasales). The median wall forms the septum; in the lateral wall there are entrances to paranasal sinuses. Towards the back, the nasal cavities open via the choanae to the nasal part of the pharynx.
In humans, three turbinates are usually distinguished:
- superior turbinate (concha nasalis superior, in animals concha nasalis dorsalis)
- middle turbinate (Concha nasalis media)
- inferior turbinate (Concha nasalis inferior, in animals Concha nasalis ventralis)
Occasionally, an upper nasal concha nasalis suprema may also be formed.
The turbinates delimit three nasal passages:
- upper nasal meatus (meatus nasi superior, in animals meatus nasi dorsalis): between the superior and middle turbinates. In non-primates it ends blindly. The olfactory organ (organum olfactorium) is located in the posterior part of this duct, which is why the duct is also called the olfactory duct.
- middle nasal meatus (Meatus nasi medius): between the inferior and middle turbinates. The middle nasal meatus also ends blindly in non-primates. The paranasal sinuses (Sinus paranasales) are connected to it, therefore also called sinus duct.
- Inferior nasal meatus (Meatus nasi inferior, in animals Meatus nasi ventralis): between the palate and the inferior turbinate. It leads into the nasopharynx via the choanal opening and serves as an airway, hence also called the respiratory duct. In the anterior part, the nasolacrimal duct (Ductus nasolacrimalis) opens with a mucosal fold (Hasner's valve).
In primates, including humans, all three nasal passages lead into the nasopharynx via the choana opening and serve as an airway. Compared to non-primates, the nose is shortened and significantly higher, the nasal conchae are reduced and simpler in shape.
· 
Frontal section of a computed tomography of the nasal cavity and sinuses
· 
Frontal section through the nasal cavity
· 
Sagittal section View to the side (lateral) of the lateral wall (in the direction of the maxillary sinus)
· 
Sagittal section, with the conchae removed.
· 
Sagittal section, looking inwards (medially) at the nasal septum
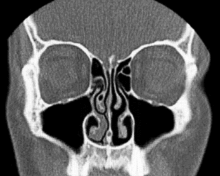
Nasal turbinates in CT (coronary stratification)
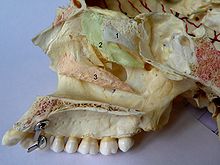
Human nasal turbinates. 1 upper, 2 middle, 3 lower turbinates

Sagittal section through a horse skull. 1 upper, 2 middle, 3 lower turbinate
Search within the encyclopedia