Asia
Asia
.svg.png)
![]()
Asia, part of Eurasia, is the largest continent in terms of area, covering some 44.6 million square kilometres, about one third of the total land mass. With over four billion people, more than half the world's population, this part of the world is also the most populous. There are 47 internationally recognized states in Asia.
In human history, Asia played an important role early on. The first great empires arose here as early as 900 BC with the Neo-Assyrian Empire or 500 BC with the even larger Achaemenid Empire.
Etymology
The word "Asia" goes back via the Latin Asia to the Greek Ἀσία (Asía). About the further origin can only be speculated until today. It is usually assumed an origin of the Assyrian assu "sunrise, east". The name Asía would name an eastern region, which lies in the direction of the sunrise, and would correspond to the Latin word Orient or the German "Morgenland". The early Greeks at first called only the land mass of Asia Minor Asia, which later gave rise to the name of the Roman province Asia. Pliny the Elder (Naturalis historia, c. 77 AD) then applied the name to the larger continent. In the long run, the old Asia became Asia minor.
In Greek mythology, Asia was the name of an Okeanide (or mother of one in Hesiod), after whom in turn the geographical region was supposed to have been named. According to Aeschylus (Promētheús desmṓtēs, c. 470 BC) she is also the wife of the Titan Iapetos and mother of Prometheus, according to Herodotus (Histories, 5th century BC) his wife.
In today's common usage, the terms Asian and Asians refer primarily to things and people of East or Southeast Asian origin, for example in relation to cuisine, philosophy or architecture, sometimes with the inclusion of India, while the terms very rarely also refer to the countries west of India. While West Asia had been in close contact with Europe since ancient times, this was not the case with East Asia, so that this region represented the epitome of foreignness in Europe for centuries, also because countries such as China and Japan separated themselves from the outside world and showed only limited interest in exchange (cf. Sinocentrism, closing offJapan).
Geography
→ Main article: Geography of Asia
Asia is the largest continent on earth. With an area of approximately 44.6 million square kilometers (excluding Russia 31.7 million square kilometers), it comprises about one third of the total land mass. Together with Europe, Asia is also considered part of the large continent of Eurasia.
The continental landmass is located entirely in the Eastern Hemisphere and north of the equator, except for the most southeastern islands in the Malay Archipelago, which are located in the southern hemisphere of the Earth. The Chukchi Peninsula in eastern Siberia is east of the 180th parallel, but eastern time +12h applies.
Extension
Asia is bounded by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Indian Ocean to the south.
Asia has no clear geographical or geological border in the west with respect to Europe. The most common definition of the border with Europe from north to south: the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Caucasus or Manytschniederung, the southern coast of the Black Sea, as well as the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles. From the Barents Sea to the Black Sea, this border is about 2700 km long.
Asia is connected to Africa north of the Red Sea via the Sinai Peninsula (isthmus of Suez, 145 km wide).
In the northeast, the mainland masses of Asia and North America lie just over 80 km apart at the Bering Strait. In the southeast, the Malay Archipelago forms the connection to Australia. The southernmost point is the Indonesian island of Pamana.
The northernmost mainland point of Asia and Earth is Cape Chelyuskin on the Taimyr Peninsula (77° 43′ 21″ N), the easternmost point Cape Deshnyov on the Chukchi Peninsula (169° 39′ 7″ W). From there to the westernmost point of Asia, Cape Baba in Asia Minor (26° 3′ 50″ E), it is 8,223 km as the crow flies. The southernmost mainland point of the Asian continent is Cape Tanjung Piai on the Malay Peninsula (1° 15′ 57″ N).
Structure
There are various approaches to the regional classification of Asia. The following subdivision into regions is used, among others, by the UN statistical agency UNSD. This division of Asia into regions by the United Nations is done for statistical reasons only and does not imply any assumption about political or other affiliations of the countries and territories.
- North Asia
- Central Asia
- Near East (West Asia)
- South Asia
- East Asia
- Southeast Asia
In some publications, these boundaries are varied, depending on the goal, topic, and background for which a division is used. In the past, Afghanistan was assigned to Central Asia, now to South Asia. There are also alternative or additional subdivisions or overlaps, for example for Northeast Asia.
flora and fauna
The main vegetation zones or ecozones (from north to south):
- Treeless tundra north of the Arctic Circle. The most important animals for the nomadic inhabitants like those of the Nenets are the reindeer.
- Temperate zone forests, including the boreal coniferous forest (taiga) in Siberia roughly between the Arctic Circle and the course of the Trans-Siberian Railway, and deciduous forests roughly in the Far East and in the Caspian Sea area. The diverse fauna is (historically) important for hunting, and in addition to agriculture and livestock breeding, the use of wood is also important. For example, the rare Amur tiger and Amur leopard live here, as well as deer, wild boar, lynx and bears.
- Continental grasslands or steppes. Animal species that naturally inhabit these steppes include wild horses, saiga antelope, mongoloid cells, wolves and gopher.
- Vegetation-poor, rocky mountain landscapes and desert landscapes. Highland climate with large daily temperature variations and plenty of sunshine. The mountains are populated by numerous mountain grazing animals such as ibex, gorals, serau and wild sheep. The most important predator of the Central Asian mountains is the snow leopard. The desert areas are home to half-elk, wild camels, cheetahs and gazelles.
- Tropical savannah areas and dry forests, preferably on the Indian subcontinent, but also in Southeast Asia. Characteristic large animals are lions, deer goat antelopes, Nile Gau antelopes and various deer.
- Tropical rainforests. After clearing, the next step of destruction is often the cultivation of monocultures such as palm oil plantations, e.g. in Sabah (Malaysia) on Borneo.
- Tropical monsoon areas such as the Mekong Delta: Here rice cultivation dominates and poultry and pigs as well as fishing are the livestock.
See also: "Flora and Fauna" in the article Geography of Asia
Superlatives
Asia boasts a number of global geographic superlatives:
- the most populous country: China
- the largest share of the world's largest country by area: Russia. This share of Russia itself is larger than the world's second largest country Canada.
- the highest mountain range: Himalaya, all mountains above 8000 meters peak height
- the deepest and oldest inland lake: Baikal
- the largest inland lake: the Caspian Sea
- the deepest body of water: the Dead Sea
It is the continent with the most diverse vegetation, varying from the permafrost of Siberia to the jungles of Southeast Asia. In addition to the extremes of tundra, desert and tropical rainforest, all other vegetation zones represented on earth are also found in Asia.
Another distinctive feature are most of the intercontinental states of the world, with both Asian parts of the country and territories in other parts of the world. These include Russia, Kazakhstan, Indonesia, Japan, Egypt and Turkey.
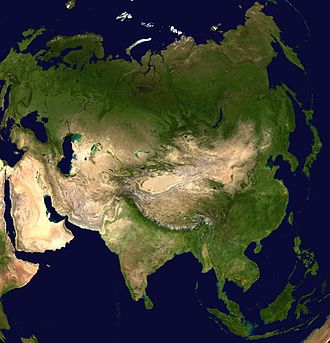
Satellite image of Asia
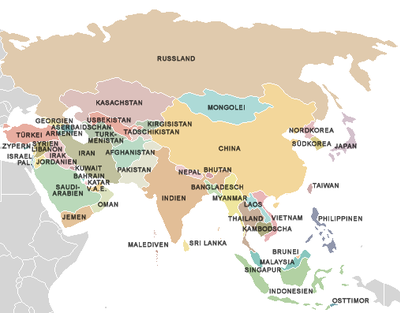
Asian countries

Tundra in the territory of the Nenets on the lower reaches of the Yenisei River
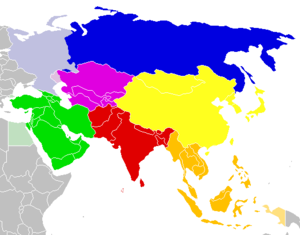
Division of Asia into regions by the UNSD North Asia Central Asia Near East (West Asia) South Asia East Asia Southeast Asia
Questions and Answers
Q: Where is Asia located?
A: Asia is mainly located in the northern hemisphere of the Earth.
Q: Does Asia share a continent with any other region?
A: Yes, Asia is connected to Europe in the west, forming a continent called Eurasia.
Q: Which are some of the oldest human civilizations that began in Asia?
A: Some of the oldest human civilizations that began in Asia include Sumer, China, and India.
Q: Were there any large empires in Asia?
A: Yes, Asia was home to some large empires such as the Persian Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Mongol Empire, and the Ming Empire.
Q: How many countries are in Asia?
A: Asia is home to at least 44 countries.
Q: Are there any countries that are partly considered European in Asia?
A: Yes, Turkey, Russia, Georgia, Kazakhstan and Cyprus are partly considered European in Asia.
Q: Is Asia viewed as a separate continent from Europe?
A: Sometimes, Asia is viewed as a separate continent from Europe although it is connected to it.
Search within the encyclopedia