Mongolian language
![]()
This article is about the language in Mongolia and Inner Mongolia; for other Mongolian languages, see Mongolian languages.
The Mongolian language (in Mongolian script: ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ
ᠬᠡᠯᠡ, in Cyrillic script: монгол хэл) in the strict sense belongs to the family of Mongolian languages, together with some closely related languages (notably Buryat and Oirat/Calmongolian). Mongolian is spoken by a total of about 4.5 to 5 or slightly more than 5 million people, depending on the estimate, of whom slightly less than half (2 to 2.4 million, depending on the estimate) live in the state of Mongolia, slightly more than half (just under 3 to 3.4 or 3.5 million, depending on the estimate) live in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and adjacent provinces in China, and smaller groups live in the Russian Federation (mainly in Buryatia, but also in neighboring Tuvinia).
There are two standard varieties of Mongolian: one in Inner Mongolia, which is written in the traditional Mongolian script and is the official language there alongside Chinese, and the official language in the state of Mongolia, which is written in a Cyrillic alphabet.
Play media file A person who speaks Mongolian
Classification and geographical distribution
For classification see also: Mongolian languages
The family of Mongolian languages can be divided as follows:
- The Dagur branch in the northeast consists of Dagur (Daur) with several variants (the Amur, Nonni, and Hailar dialect groups, as well as a diaspora in the Ili area since the 18th century).
- The common Mongolian branch of the Mongolian languages includes idioms in the traditional homeland of the Mongols (Mongolia), but also in the north (Siberia), east (Manchuria/Northeast China), south (Ordos), and west (Dsungarei). It is a dialect continuum that is usually understood by its speakers as a common Mongolian language. This view is also shared by most Mongolian scholars in Mongolia State and Inner Mongolia, as well as the official categorization of ethnic groups in China, while Russian and Western scholars consider at least Buryat and Oiratic, and often Ordos and Chamnigan, to be separate languages (see below). This is ultimately a question of definition and terminology.
- The Shirongol branch in Qinghai includes West Yugur, Monguor, Bonan, Kangjia and Santa (Dongxiang).
- The Moghol branch in Afghanistan consists of Moghol with several (possibly extinct) variants.
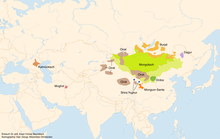
Geographical distribution of Mongolian languages
Dialects
- The Chalcha dialects (Mongolian [xɑlx] ᠬᠠᠯᠬ ᠠ 'qalq-a' / Халх 'Xalx') in the centre of the linguistic area cover approximately the territory of the state of Mongolia, but also include some dialects - v. especially Qahar ([ˈʧɑxɑ̆r] ᠴᠠᠬᠠᠷ 'čaqar' / Цахар 'Caxar') - in Inner Mongolia. They are the basis of the two modern standard Mongolian languages.
- The Horqin dialects ([ˈxɔrʧɪn] ᠬᠣᠷᠴᠢᠨ 'qorčin' / Хорчин 'Xorčin') are spoken in eastern Inner Mongolia as well as in the neighboring Chinese provinces of Liaoning, Jilin, and Heilongjiang.
- The Ordos dialects ([ˈɔrdɔ̆s] ᠣᠷᠳᠣᠰ 'ordos' / Ордос 'Ordos') are spoken on the Ordos Plateau in southern Inner Mongolia between the Great Wall of China and the Great Bend of the Yellow River (Huang He).
- Chamnigan (ᠬᠠᠮᠨᠢᠭᠠᠨ 'qamniɣan') is spoken in the northeast, in the valleys of the Onon and Argun rivers in the border region between Russia (Transbaikal), China (Hulun Buir), and Mongolia (Chentii Aimag).
- Buryat ([ˈburɪɑd] ᠪᠤᠷᠢᠶᠠᠳ 'buriyad') is spoken in the north, on both sides of Lake Baikal, especially in the Republic of Buryatia, but also as far north as Mongolia and China (in the two Bargu banners in Hulun Buir). Buryat is now a written language in its own right, though not used by Buryats in Mongolia and China.
- Oiratic ([œːrd] ᠣᠶᠢᠷᠠᠳ 'oyirad') originally had its center in Dsungarei in northern present-day Xinjiang, but is spoken as far west as Mongolia (Chowd-Aimag) and Inner Mongolia (Alxa) and northern Qinghai (Haixi), as well as by a diaspora in the Volga region (Kalmyk) and Manchuria. Kalmyk is now a written language in its own right.
Search within the encyclopedia