Milan
![]()
The title of this article is ambiguous. For other meanings, see Milan (disambiguation).
Milan (Italian Milano [miˈlaːno], Lombard Milan [miˈlã(ŋ)], Latin Mediolanum) is the second-largest city in Italy, with a population of about 1.4 million, and the capital of the Lombardy region and the metropolitan city of Milan. The metropolitan region was Italy's largest metropolitan area in 2006, with 7.4 million inhabitants.
Once a foundation of Celtic settlers, the city experienced rapid growth during the Roman Empire. Milan has been under the influence of German, French and Austrian emperors throughout its history and grew into the country's largest industrial city after the unification of Italy. It is now Italy's leading cultural, media and fashion capital, a university city and an international financial centre as the seat of the Italian Stock Exchange. It is home to a World Heritage Site, historically significant buildings and diverse art treasures that attract several million tourists a year. Thanks to its convenient location on the Po Valley in northern Italy, the trade fair city is a hub of the rail and motorway network and Italy's second largest aviation hub with three international airports.
Geography and climate
Geographical position
Milan is located in the northwestern Po Valley, roughly midway between the Po River in the south and the foothills of the Alps in the north. The core city is located on a largely flat plain, with the highest point at 122 m above sea level. Two rivers run through the city: the Olona to the west and the Lambro to the east. Medieval canals, the Navigli, connect Milan with the lakes of northern Italy and the Lombard rivers, and were of vital importance to the local economy until the mid-20th century.
The urban area covers 182 km² with 1,343,230 inhabitants. The Milan agglomeration, with a total of over five million inhabitants, includes numerous suburbs that extend mainly to the north to Varese, Como, Lecco and Bergamo. Over 7.6 million people live in the metropolitan region.
Adjacent municipalities are Arese, Assago, Baranzate, Bollate, Corsico, Peschiera Borromeo, Rho, Sesto San Giovanni, Cormano, Cologno Monzese, Bresso, Novate Milanese, Vimodrone, Pero, Segrate, Settimo Milanese, Cusago, Cesano Boscone, Trezzano sul Naviglio, San Donato Milanese, Buccinasco, Rozzano and Opera.

enlarge and show information about the picture
![]()
Milan seen from the Milan Cathedral
City breakdown
Milan is divided into nine municipalities (municipi). The original twenty districts were reduced in 1999. Today, Zona 1 includes the historic city centre, all other eight districts are arranged as circular segments clockwise around the old town. Milan's boroughs are given partial sovereign status by a district council (Consigli di Zona) and a district president, including in financial administration.
- Municipio 1: Centro Storico (city centre)
- Municipio 2: Stazione Centrale (Central Station), Gorla, Turro, Greco, Crescenzago
- Municipio 3: Città Studi, Lambrate, Porta Venezia
- Municipio 4: Porta Vittoria, Forlanini
- Municipio 5: Vigentino, Chiaravalle, Gratosoglio
- Municipio 6: Barona, Lorenteggio
- Municipio 7: Baggio, De Angeli, San Siro
- Municipio 8: Fiera, Gallaratese, Quarto Oggiaro
- Municipio 9: Garibaldi, Niguarda
Climate
Milan is located in a subcontinental east side climate. The Alps and the Apennines form a natural barrier against weather influences from northern Europe and the Mediterranean. As in many parts of northern Italy, very warm to hot summers, moderately cold, rainy winters and high humidity throughout the year are typical. In the winter months there is often heavy fog formation, occasionally snowfall, and in summer temperatures often rise to 35 °C and more, especially in July and August. The weather is noticeably influenced by the Föhn, which occurs especially in spring. Strong hurricane-like storms can also occur at this time. The lowest measured temperature is -17.3 °C, the highest 40.4 °C.
| Milan, Lombardy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monthly average temperatures and precipitation for Milan, Lombardy
Source: WMO 1961-1990; humidity, sunshine duration: wetterkontor.de | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
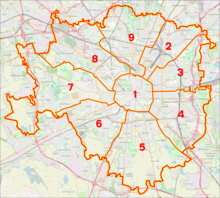
The nine districts of Milan
Etymology
The name Milan derives from the Italian Milano, which came from the original Latin Mediolanum, meaning "in the middle of the plain". The place name probably goes back less to Latin medius "situated in the middle" and planus "plain" than to the synonymous Gallic-Celtic roots *medios and *lanu. The same is true of the Lombard name Milàn. Milan's inhabitants call themselves Milanées or Meneghìt.
Search within the encyclopedia