Michigan
![]()
The title of this article is ambiguous. For other meanings, see Michigan (disambiguation).
Michigan (English pronunciation [![]()
![]() ˈmɪʃɪgən], Ojibwe for "Great Lake") is a state of the United States. It is known as the birthplace of the automobile industry, but also has a large tourism industry. Destinations such as Traverse City, Mackinac Island, and the entire Upper Peninsula attract sportsmen and nature lovers, especially from all over the United States and Canada. Michigan, which consists of two large peninsulas, has the longest freshwater coastline of any U.S. state due to its location on the Great Lakes. Michigan has the sobriquets Great Lakes State 'Great Lakes State', Wolverine State 'Wolverine State', Mitten State 'Mitten State' and Water Winter Wonderland 'Water Winter Wonderland'.
ˈmɪʃɪgən], Ojibwe for "Great Lake") is a state of the United States. It is known as the birthplace of the automobile industry, but also has a large tourism industry. Destinations such as Traverse City, Mackinac Island, and the entire Upper Peninsula attract sportsmen and nature lovers, especially from all over the United States and Canada. Michigan, which consists of two large peninsulas, has the longest freshwater coastline of any U.S. state due to its location on the Great Lakes. Michigan has the sobriquets Great Lakes State 'Great Lakes State', Wolverine State 'Wolverine State', Mitten State 'Mitten State' and Water Winter Wonderland 'Water Winter Wonderland'.

Michigan, border sign
Geography
Relief
Michigan is the only state in the USA whose mainland is divided into two parts. Lake Michigan stretches between the parts. Upper Michigan, the northern part, is located between Lake Michigan in the south and Lake Superior in the north. The western part is characterized by the Superior Upland, an upland of granitic bedrock. It consists of several mountain ranges running northeast to southwest, extending west into Wisconsin and Minnesota. Individual mountain ranges include the Porcupine Mountains and the Gogebic Range and Copper Range. The Superior Upland has much greater elevation changes than the rest of the state. Michigan's highest elevation is Mount Arvon at 603 m. Isle Royale in Lake Superior, although both the Canadian province of Ontario and the US state of Minnesota are much closer to the island, is also part of Michigan.
The southern part, Lower Michigan, is located between Lake Michigan (west) and Lake Huron (east). Area-wise, this is the larger part of the state. The vast majority of the state's population lives in the southernmost third of Lower Michigan. All of Lower Michigan and the eastern part of Upper Michigan are part of the Eastern Great Lakes Lowland. This is a flat to rolling lowland and was formed as a result of the glaciers that covered the land during the Ice Age. The average elevation is 274m and the lowest point is about 173m. Consequently, there are hardly any noticeable differences in altitude within Lower Michigan.
Floor
The soil in Upper Michigan is gray-brownish and acidic. It originated from glacial deposits and is partly not very fertile. Because of this and the climate, there is little agriculture there. In southeastern Michigan, on Saginaw Bay, a heavy, loamy soil predominates. Most of Lower Michigan, however, has very fertile soil, which is also used for agriculture.
Rivers and lakes
Michigan shares in four of the five Great Lakes. These are Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, Lake Superior and Lake Erie. This gives it a total coastline of 5310 km. There are also more than 11,000 smaller lakes, the largest of which is Houghton Lake in northern Lower Michigan.
The longest river in the state is the Grand River. Other important rivers are the Kalamazoo, Manistee, Saint Clair, Detroit and Saint Joseph. Through the waterways, goods can be shipped all over the world, as there is a connection to the Atlantic Ocean via Lake Erie and the Saint Lawrence River. In Upper Michigan there are several waterfalls, for example the Tahquamenon Falls.
Climate
The climate in Michigan has a special position compared to the rest of the United States. This is due to its proximity to the Great Lakes. These give Michigan a milder climate compared to other states of the same latitude. It is humid and continental (quite a rare combination worldwide) and is in the cool temperate climate zone. However, the climates of Upper and Lower Michigan should be considered separately.
Upper Michigan is much cooler and has a northern climate. The average frost-free period is only 60 to 120 days per year. Winters are very severe and summers are mild. The average annual temperature in Sault Ste. Marie near the border with Canada in northeastern Upper Michigan is 4.3 °C. Warmest month is July with 18 °C, the coldest are January and February with -10 °C. The average annual precipitation is 869 mm and is distributed throughout the year.
The climate in Lower Michigan, on the other hand, is mild. The average frost-free period is 180 to 240 days, which is significantly longer than in Upper Michigan. In Detroit (in southeastern Lower Michigan), the average temperature is 10 °C. Warmest month is July with 24 °C, coldest is January with -5 °C. Overall, temperatures are 5 °C higher than in Upper Michigan. The temperature difference is low for a continental state at 18 °C. This is due to the influence of the Great Lakes. In the summer they cool the air and in the winter they retain heat and warm the air. However, the temperature difference is still significantly higher than, for example, on ocean coasts, which is why the Michigan climate is counted as continental type despite the influence of the lakes. Precipitation is also year-round here, but somewhat lower at 691 mm.
Neighbouring countries
Michigan has land borders with Ohio and Indiana to the south. In addition, the Upper Peninsula has a land border with Wisconsin to its southwest. There is also a border with Illinois across Lake Michigan and a border with Minnesota across Lake Superior. The border with the Canadian province of Ontario runs through Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Lake Erie and their connecting waters.
While there is no land border with Illinois, the southwestern part of the state is still part of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is quicker to reach from there than Detroit.
Largest cities

- List of all municipalities in Michigan (in alphabetical order)
- List of cities in Michigan by population (over 10,000 residents).
Structure
- List of counties in Michigan
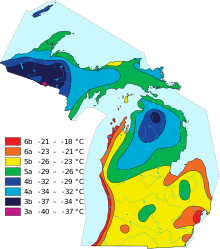
USDA Climate Zones in Upper and Lower Michigan.
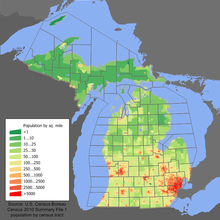
Population density
Economy
Michigan's economic output in 2016 was $487 billion, making it the thirteenth-highest economic output of any state in the U.S. and accounting for 2.64% of the total U.S. economy. Counted as a separate country, Michigan's economic output would be about the same as Poland's. Real per capita GDP in 2016 was USD 49,074 (national average of the 50 US states: USD 57,118; national ranking: 37). The unemployment rate was 4.6% in November 2017 (national average: 4.1%).
Industries
Michigan has a diverse economy. The primary (agriculture/mining) and secondary (industry) sectors are of utmost importance to the economic area. In the first half of the 19th century, agriculture gained great importance in Michigan, which continues today. Major agricultural products include dairy products, corn, soybeans, and cattle. In addition, Michigan is a leader in the production of cherries and apples. About $3 billion is collected from crops. The timber industry does not play a significant role. It is carried on mainly in western Upper Michigan; the lumber is used mostly for papermaking. Fishing also contributes little to the economy. The value of the annual catch is only 11 million US dollars.
Mining plays a supporting role for Michigan. It is an important pillar for the industry. There are abundant deposits of ores, and natural gas and petroleum are also produced in the North Central and South. The principal commodities are iron ore, petroleum, natural gas, and copper. The mining of salt is also very significant. In addition, Michigan is an important exporter of gravel, peat, silver and potash, which are extracted from the numerous swamps.
Michigan is one of the most important industrial states in the USA. It is a leader in the production of passenger cars. Detroit is one of the most important centers in this regard. The headquarters of the three major automobile manufacturers Chrysler, General Motors and Ford are located here. Other centers of the automobile industry are Flint, Lansing, and Pontiac. Other major industrial products include engines and construction equipment. In addition, metal alloys such as steel are manufactured, primarily in Detroit. Food processing (see: Breweries in Michigan), chemicals, and pharmaceuticals are also important. Industry in Michigan accounts for 27% of the gross national product.
The largest service sector is tourism. This industry generates $6.3 billion annually for the scenic state. There are also extensive recreational opportunities, such as water sports and summertime swimming on many Great Lakes shorelines. During the cold and relatively snowy winters, winter sports opportunities attract tourists.
Infrastructure
Michigan has a well-developed infrastructure. There is a vast network of highways totaling 189,000 km, of which 1890 km are interstate highways.
On land, goods are mostly transported via the rail network, which is still about 4000 km long today and well developed compared to other states, because many rivers are not navigable. However, many railway branch lines have been closed in the second half of the 20th century. On the coasts to the Great Lakes there are large port cities for import and export such as Calcite and Escanaba. On the Great Lakes, the Sault-Saint Marie Canals and the Saint-Clair and Detroit Rivers are important because they connect Lake Huron and Lake Erie, providing a link to the Atlantic Ocean. Furthermore, Saint Mary's is important. This connects Lake Superior with Lake Huron.
Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport is an international airport and one of the largest in the USA.
August 2020, Michigan, in cooperation with private companies, has undertaken the project launch for the commissioning of a separate lane for autonomous vehicles that is unique in the USA. The 65-kilometer stretch of highway along the Interstate 94 corridor will initially connect Detroit with the city of Ann Arbor. As a first step, a two-year study will examine the extent to which either existing lanes need to be used for this purpose or new lanes need to be built.
Questions and Answers
Q: What is Michigan?
A: Michigan is one of the fifty states in the United States of America.
Q: How big is Michigan?
A: Michigan is the 11th largest state in the United States.
Q: What is unique about Michigan's geography?
A: Michigan is made up of two peninsulas connected by the Mackinac Bridge, making it the only state to be so.
Q: What states does Michigan border?
A: Michigan borders the U.S. states of Wisconsin, Indiana, Ohio, Minnesota, and Illinois.
Q: How does Michigan border Minnesota and Illinois?
A: Michigan's borders with Minnesota and Illinois are only by water.
Q: Does Michigan border Canada?
A: Yes, Michigan borders Canada by water.
Q: When did Michigan become a state and what accomplishment did it make in 1847?
A: Michigan became the 26th state to join the union on January 26, 1837. In 1847, Michigan became the first U.S. state to abolish the death penalty.
Search within the encyclopedia