Imperial China
![]()
This article is about the empire that existed until 1912. For the later restoration attempt, see Imperial China (1915-1916).
The Empire of China was founded in 221 BC by Emperor Qin Shihuangdi. He formed it from several kingdoms that he had gradually conquered. In its long history, the empire broke up several times into at times numerous constituent states and was reunited three times: in 280 by the Jin dynasty, in 589 by the Sui dynasty and in 1279 by the Mongol Yuan dynasty.
The empire existed (with interruptions) for 2132 years until the proclamation of the Chinese Republic by Sun Yat-sen on January 1, 1912; the last emperor, Aisin Gioro Puyi, abdicated on February 12, 1912. Yuan Shikai, the first president of the Republic of China, made himself "Emperor of China" in 1915. This "empire", which was already abolished in 1916, and later attempts at restoration are of little historical significance.
The partly mythical rulers of the early period (see Chinese mythology) have been included in historiography and are sometimes referred to as "original emperors" (Chinese partly as huang, 皇, partly as di, 帝), especially in Western accounts. In the strict historical sense, they were not emperors (huangdi, 皇帝). The rulers of the pre-imperial Zhou dynasty are considered kings (wang, 王).
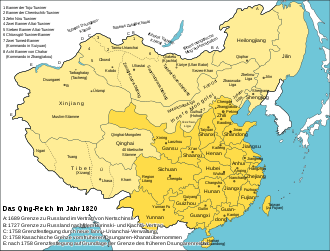
Imperial China at the time of the Qing Dynasty, 1820
Traditional chronology of the ruling dynasties
→ Main article: History of China and Chronology of China
There have been various dynasties in Chinese history. The partly mythological "dynasties" before the emergence of China as a unitary state - that is, precisely before the founding of the Chinese Empire - were:
| Dynasty | Pinyin | Time span | Ruler | |
| The Three Exalted Ones and the Five Primordial Emperors | Sān Huáng Wǔ Dì | ?-2184 BC. | Rulers List | |
| Xia dynasty | Xia Chao | ca. 2200-1800 B.C. | Rulers List | |
| Shang Dynasty | Shāng Cháo | ca. 1500-1100 BC | Rulers List | |
| Zhou Dynasty | Zhōu Cháo | 1122/1045-770 BC Western Zhou Dynasty | Rulers List | |
| 770-256 B.C. Eastern Zhou Dynasty | Rulers List | |||
| Time of spring and autumn annals | Chūnqiū Shídài | 722-481 BC. | - | |
| The Time of the Disputing Empires | Zhànguó Shídài | 475-221 BC. | - |
The dynasties of the Empire of China, founded in 221 BC by the ruler of the then Kingdom of Qin (秦國) and unifying the whole empire for the first time, were:
| Dynasty | Pinyin | Time span | Ruler | |
| Qin Dynasty | Qín Cháo | 221-207 BC. | Rulers List | |
| Han Dynasty | Hàn Cháo | 206 B.C.-9 A.D. (First Reign) | Rulers List | |
| 23 A.D.-220 A.D. (Second Reign) | ||||
| Xin Dynasty | Xīn Cháo | 9-23 (Interregnum) | Rulers List | |
| Time of the Three Kingdoms | Sān Guó | 220–280 | Ruler list2 | |
| Jin Dynasty | Jìn Cháo | 265–420 | Rulers List | |
| Sixteen kingdoms | Shíliù Guó | 304–439 | Ruler list3 | |
| Southern and Northern Dynasties | Nán Běi Cháo | 420–581 | Ruler list4 | |
| Sui Dynasty | Suí Cháo | 581–618 | Rulers List | |
| Tang Dynasty | Táng Cháo | 618–907 | Rulers List | |
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms | Wǔdài Shíguó | 907–979 | Rulers List | |
| Liao Dynasty | Liáo Cháo | 916–1125 | Rulers List | |
| Song Dynasty | Sòng Cháo | 960–1279 | Rulers List | |
| Jin Dynasty | Jīn Cháo | 1125–1234 | Rulers List | |
| Western Xia Dynasty | Xī Xià | 1038–1227 | Rulers List | |
| Yuan Dynasty | Yuán Cháo | 1279–1368 | Rulers List | |
| Ming Dynasty | Míng Cháo | 1368–1644 | Rulers List | |
| Qing Dynasty | Chinese river dolphin | 1644–1912 | Rulers List |
See also
- Chinese urban development
- Names of Chinese emperors
- President of the Republic of China (Heads of State after 1912)
- List of the Presidents of the People's Republic of China (Heads of State since 1949)
Questions and Answers
Q: What was Imperial China?
A: Imperial China was a period of Chinese history that lasted over 2,000 years.
Q: When did Imperial China begin?
A: Imperial China began with Qin Shi Huang's uniting of China under the Qin dynasty in 221 BC.
Q: When did Imperial China end?
A: Imperial China ended with the overthrow of the Qing dynasty in 1911.
Q: What features of Chinese civilization spread throughout China during Imperial China?
A: Confucianism, standardized testing, standardized weights and counting systems, trade routes, and Chinese characters spread throughout China during Imperial China.
Q: How was China ruled during Imperial China?
A: China was ruled by many different dynasties, including the Qin, Han, Sui, Tang, Song, Yuan/Mongol, Ming, and Qing/Manchu dynasties, and there were also several periods where China had been ruled by several different kingdoms.
Q: Who were the rulers of Imperial China?
A: Throughout most of Imperial China, China had been ruled by emperors and empresses who were Han Chinese. However, there were some dynasties where the ruling class was made of Chinese minority groups, such as the Yuan and Qing dynasties which were ruled by the Mongols and Manchus in that same order.
Q: What was China known for during Imperial China?
A: China became known worldwide for features such as Confucianism, standardized testing, standardized weights and counting systems, trade routes, and Chinese characters during Imperial China.
Search within the encyclopedia