Hypobromite
Hypobromites are the salts of hypobromous acid. Bromine is present in the oxidation state +1.
Hypobromites can be obtained by reacting bromine with alkalis. Molecular bromine disproportionates to bromide and hypobromite. The hypobromite salt can then be separated from the bromide salt by crystallization.
In bromine water this disproportionation also takes place, which is why it reacts weakly acidic.
Hypobromites are not stable and disproportionate to bromides and bromates, which is why they must be prepared and stored at 0 °C.
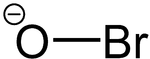
The hypobromite ion
Usage
Hypobromites are used in the chemical laboratory as a reagent in the Hofmann rearrangement. In this process, primary amines are formed from carboxylic acid amides.
See also
- Bromides: Br-
- Bromites: BrO2-
- Bromates: BrO3-
- Perbromates: BrO4-
Questions and Answers
Q: What is hypobromite?
A: Hypobromite is an ion with the chemical formula BrO-.
Q: What is the oxidation state of the bromine atom in hypobromite?
A: The oxidation state of the bromine atom in hypobromite is +1.
Q: Is hypobromite an oxidizing agent?
A: Yes, hypobromite is an oxidizing agent.
Q: What are hypobromites?
A: Hypobromites are the salts of hypobromous acid.
Q: What is the function of hypobromite?
A: Hypobromite is a disinfectant and is used to kill germs in pools and by white blood cells to fight infections.
Q: How is hypobromite made?
A: Hypobromite is made by dissolving bromine in a basic solution.
Q: What happens when hypobromite is heated?
A: When hypobromite is heated, it disproportionates to bromate and bromide.
Search within the encyclopedia

