Hindi
![]()
This article describes the language. For namesakes, see Hindi (disambiguation).
Hindi (हिन्दी hindī /ɦind̪iː/) is an Indo-Aryan, thus at the same time Indo-Iranian and Indo-European language, spoken in most North and Central Indian states and derived from the Prakrit languages. It has been the official language of India (along with English) since 1950. Hindi is closely related to Urdu.
Among the most spoken languages in the world, Hindi ranks third after Chinese and English, ahead of Spanish. Over 600 million people in and around India use it as their mother tongue or everyday language. In Fiji, more than a third of the population speaks Fiji Hindi; in Guyana and Suriname, a minority speak it, though it is rapidly losing speakers, especially in Guyana (Surinamese Hindi is sometimes considered a single language).
Hindi is written in Devanagari and contains many book words from Sanskrit. In contrast, Urdu, as the official language of Pakistan, is written in Arabic characters and has incorporated many words from Persian, Turkish and Arabic. Both are varieties of Hindustani.
The use of words of different origins has long been the subject of national political aspirations. Hindu nationalists systematically replace words of Arabic origin with borrowings from Sanskrit to emphasize their cultural distinctiveness. Similar efforts to promote Sanskrit have been in the form of Popular Sanskrit. There are also a variety of local dialects of Hindi.
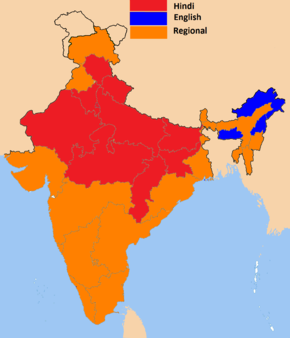
Official languages in the Indian states
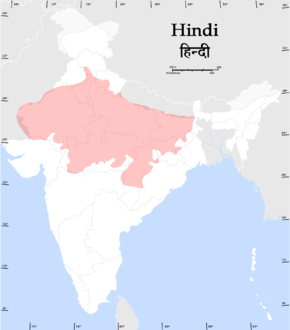
Approximate distribution area of Hindi

Typewriter keyboard with Devanagari characters
Etymology
The word hindī is of Persian origin and means "Indian". It was originally used by pre-Islamic Persian merchants and ambassadors in northern India to refer to the predominant language of northern India, Hindustani. It was later used at the Mughal court to distinguish the local language of the Delhi region from Persian, the official language of the court at the time.
Development
Origin
As with many other Indian languages, Hindi is thought to have evolved from Prakrit by way of the so-called Apabhramsha. Hindi emerged as a local dialect, like Braj, Awadhi and finally Khari Boli after the turn of the 10th century.
In comparison with Sanskrit, the following changes, among others, have occurred, some of which are already found in Pali:
- frequent omission of final 'a' and other vowels (shabda- > shabd 'word')
- Loss of 'r' in some compounds (trīni > tīn 'three').
- Reduction of consonant bundles (sapta > sāt 'seven')
- Failure of nasal consonants with retained nasalization (shānta- > shā̃t 'quiet').
Persian and Arabic influence
In 1000 years of Islamic influence, many Persian and Arabic words entered Khari Boli. Since almost all Arabic loanwords were also absorbed via Persian, they have not preserved the original Arabic phonetic status.
Portuguese loan words
From Portuguese, some loanwords are still found in Hindi today; the Portuguese phonetic stand can be used well in Hindi, as in mez < mesa 'table', pãv < pão 'bread', kamīz < camisa 'shirt'.
English loan words
In Hindi today, many words originating from English are used, such as ball, bank, film hero, photo. Some of them, however, are hardly used in modern English. Due to older and more recent borrowings as well as purely Indian neologisms, a large number of synonyms have arisen for some terms: leṭrīn < latrine = urinal = ṭoileṭ 'toilet' (in addition, there are the words peshāb-khānā, pā-khānā, originally from Persian, and the formal expressions svacchālaya, shaucālaya).
Many older borrowings have already been adapted to the Indian phonetic standard, including:
- boṭal < bottle 'bottle'
- kampyūṭar < computer
- ãgrezī < English
- pulis < police 'police
- reḍiyo < radio
- prafessar < professor.
The dentals in particular were retroflexed in Hindi, which is easy to hear when Indians speak English.
Some English loan words have been combined with Indian words to form new terms: photo khī̃cnā 'photograph', fry karnā 'fry', shark-machlī 'shark'.
Hindi as a donor language
Words have also passed from Hindi into other languages, Hindi being partly the original language and partly only an intermediary language. Hindi words in German include: Bungalow (bãglā), chutney, jungle, kohl, cummerbund, monsoon (the Hindi word mausam itself being a loanword from Arabic), punch, shampoo (cāmpnā 'massage'), veranda.
Search within the encyclopedia