Fort Knox
![]()
This article or subsequent section is not sufficiently supported by evidence (e.g., anecdotal evidence). Information without sufficient evidence may be removed in the near future. Please help Wikipedia by researching the information and adding good supporting evidence.
37.8833333333-85.9652777778Coordinates: 37° 53′ 0″ N, 85° 57′ 55″ W
![]()
The title of this article is ambiguous. For other meanings, see Fort Knox (disambiguation).
Fort Knox is a U. S. Army base in the U. S. state of Kentucky. It is best known as the storage facility for the United States Treasury's gold reserve, known as the United States Bullion Depository. Fort Knox is home to one of the largest quantities of gold in the world. However, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, it holds even more gold, including that of foreign banks and central banks.
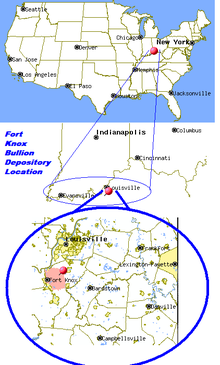
Fort Knox
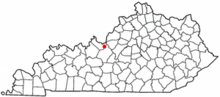
Location of Fort Knox in Kentucky
History
The fort was built in 1862 during the Civil War and was then called Fort Duffield. After the war, it was neglected. During World War I, the fort was recommissioned and enlarged. In the process, it was named for Henry Knox, a Revolutionary War general and later Secretary of War. At times the fort covered an area of 162 km2. After the war, however, operations were again greatly reduced.
In the 1930s, the fort became a permanent location for armored troops. The United States wanted to catch up with the German Reich, which was heavily mechanized at the beginning of World War II. By 1943, Fort Knox consisted of 3820 buildings on a total area of 432 km2.
Stationed units
 1st Infantry Division
1st Infantry Division- 3rd Infantry Brigade Combat Team (IBCT) (Infantry Brigade)
- 3rd Logistics Command
- 19th Engineer Battalion
Search within the encyclopedia