Florida
![]()
This article is about the US state. For other meanings see Florida (disambiguation).
Florida (pronunciation American English [![]()
![]() ˈflɔːɹɪdə], also [ˈflɑːɹɪdə]; Spanish [floˈɾiða]) is a state in the southeastern United States of America. It is known as the Sunshine State. The peninsula of the same name was discovered by Spanish explorers during Easter and named after them: Easter is also called Pascua Florida in Spanish. The emblem animal of Florida is the Florida panther. The state capital is Tallahassee.
ˈflɔːɹɪdə], also [ˈflɑːɹɪdə]; Spanish [floˈɾiða]) is a state in the southeastern United States of America. It is known as the Sunshine State. The peninsula of the same name was discovered by Spanish explorers during Easter and named after them: Easter is also called Pascua Florida in Spanish. The emblem animal of Florida is the Florida panther. The state capital is Tallahassee.
Geography
Geographical position
Florida consists of the Florida Peninsula and the mainland Florida Panhandle and is located in the southeast of the United States. On the east coast lies the Atlantic Ocean, on the west and south coast the Gulf of Mexico.
The state has a chain of islands at the southern end, whose islands are called "Keys". The best known are the Florida Keys, which are connected by 42 bridges. At the end of this island chain is Key West. From there it is only 140 kilometers to Cuba. Key West is also the southernmost point of the continental USA.
With a total area of 170,304 km², Florida has the 22nd place among the states. 30,634 km² (17.99%) of the state's territory are water areas.
Extension of the national territory
Florida has a latitude of 260 km between 79° 48' W and 87° 38' W and a longitude of 800 km between 24° 30' N and 31° 00' N.
Neighbouring countries
To the north are the US states of Georgia and Alabama. It is close to Cuba, Haiti and other countries in the Caribbean. After Hawaii, it is the southernmost state in the United States.
Geology
The Florida Continental Shelf is a more than 700 km long bulge of the North American continent. The Florida peninsula is the over-sea part of this bulge, the panhandle belongs to the coastal plain of the Gulf of Mexico. The deep basement is composed of Precambrian volcanic rocks, Devonian sedimentary rocks, and later Triassic and Jurassic volcanic rocks. Above this lie young sedimentary rocks from all periods between the Jurassic and the Holocene. The structure is dominated by limestone, which is predominantly highly porous. The central aquifer, important to Florida's freshwater supply, lies within this porous limestone. Chemical erosion at the surface of the limestone results in karst features.
Florida is particularly affected by rising sea levels. In Miami Beach, sea levels have risen 23 cm since about 1920. The rising salt water is infiltrating the aquifer and has resulted in the loss of drinking water supplies since the 1990s. In addition, drainage ditches are losing their slope against the sea, making it impossible to drain flooded areas.
Climate
Florida is divided into two climate zones: the northwestern region is subtropical humid and the rest is tropical humid. In the period from June to November, Florida is often hit by sometimes violent tropical storms (hurricanes). Winters are warm with temperatures around 25 °C. Snow is very rare in Florida.
| Climate table Jacksonville | |||||||||||||
| Month | JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | YEAR |
| Day temperature °C | 18 | 20 | 23 | 27 | 30 | 32 | 33 | 33 | 31 | 27 | 23 | 19 | 26,3 |
| Night temperature °C | 6 | 7 | 10 | 14 | 18 | 21 | 23 | 23 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 7 | 14,5 |
| Sunshine hours per day | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7,3 |
| Rainy days | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 13 | 12 | 14 | 11 | 6 | 7 | 108 |
| Water temperature °C | 17 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 27 | 24 | 20 | 23 |
| Climate table Key West | |||||||||||||
| Month | JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | YEAR |
| Day temperature °C | 24 | 25 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 29 | 26 | 25 | 28,2 |
| Night temperature °C | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 23 | 20 | 19 | 22,1 |
| Sunshine hours per day | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 9,3 |
| Rainy days | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 13 | 12 | 9 | 6 | 96 |
| Water temperature °C | 24 | 24 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 25 | 27 |
| Climate table Miami | |||||||||||||
| Month | JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | YEAR |
| Day temperature °C | 24 | 25 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 27 | 25 | 28,6 |
| Night temperature °C | 15 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 22 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 24 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 20,2 |
| Sunshine hours per day | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 8,8 |
| Rainy days | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 11 | 7 | 5 | 108 |
| Water temperature °C | 22 | 22 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 28 | 26 | 24 | 26 |
| Climate table Orlando | |||||||||||||
| Month | JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | YEAR |
| Day temperature °C | 24 | 23 | 26 | 28 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 29 | 26 | 23 | 28,1 |
| Night temperature °C | 9 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 19 | 22 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 19 | 14 | 11 | 16,6 |
| Sunshine hours per day | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7,9 |
| Rainy days | 6 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 96 |
flora and fauna
In Florida, mainly subtropical humid forests grow - consisting mainly of pines and various palm species - which in the extreme south and on the southern coastal areas merge into tropical vegetation forms - here, the swamp cypress forests, the "tropical forest islands" in the Everglades swamps (hammocks) and the mangrove forests on the coast are particularly worth mentioning. In the interior, the forests partly form open areas, which are called "prairies", although they have a high proportion of woody plants as well as grasses. The state's biodiversity is among the highest in the United States.
The landscapes, some of which are still largely natural, are home to more than fifty endangered species, including the Caribbean manatee, leatherback, Atlantic bastard and hawksbill turtles, and the pointed crocodile in the waters; the mammals Florida panther (cougar subspecies), Key white-tailed deer, and Florida bulldog bat; and numerous bird species including the bald eagle.
Florida is one of the world's hotspots for invasive alien species introduced by humans. These include the mugwort ambrosia, the Asian ladybird and the dark tiger python in the Everglades. The proximity of natural areas to densely populated coastal cities with abundant tourism and commercial traffic favors this development. Not all new arrivals are necessarily harmful. In Florida, however, there are quite a few species that have become a major threat to endangered native species. The python, in particular, has proliferated enormously in South Florida, wiping out (as of 2015) up to 99 percent of existing opossums, raccoons, or marsh rabbits. The snake, which originated in Southeast Asia, was likely released by private snake keepers when importing and selling strangler snakes was still legal in Florida. Given the problem, this has since been banned. Today, the aquatic agency pays a premium for each python killed. However, given the presumed 30,000 animals, this is a losing battle.

Native alligator and foreign tiger python in battle
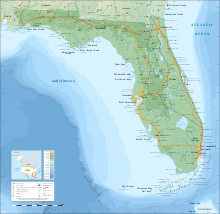
Topographic Map of Florida
Population
| Population development | |||
| Census | Inhabitants | ± in % | |
| 1830 | 34.730 | - — | |
| 1840 | 54.477 | 56,9 % | |
| 1850 | 87.445 | 60,5 % | |
| 1860 | 140.424 | 60,6 % | |
| 1870 | 187.748 | 33,7 % | |
| 1880 | 269.493 | 43,5 % | |
| 1890 | 391.422 | 45,2 % | |
| 1900 | 528.542 | 35 % | |
| 1910 | 752.619 | 42,4 % | |
| 1920 | 968.470 | 28,7 % | |
| 1930 | 1.468.211 | 51,6 % | |
| 1940 | 1.897.414 | 29,2 % | |
| 1950 | 2.771.305 | 46,1 % | |
| 1960 | 4.951.560 | 78,7 % | |
| 1970 | 6.789.443 | 37,1 % | |
| 1980 | 9.746.324 | 43,6 % | |
| 1990 | 12.937.926 | 32,7 % | |
| 2000 | 15.982.378 | 23,5 % | |
| 2010 | 18.801.310 | 17,6 % | |
| Estimate 2017 | 20.984.400 | 11,6 % | |
| Before 1900 1900–1990 2000 2010 | |||
Florida has a population of 21.47 million (as of July 2019), of which 77.3% are white (with 26.1% Hispanics and Latinos), 16.9% African American, 3.0% Asian American. Based on United States Census Bureau population estimates, Florida surpassed New York State to become the third most populous state in the United States in 2014. The two states with larger populations are California and Texas.
Religions
The population of Florida belongs mainly to various Protestant churches. However, the percentage of Catholics is increasing rapidly, mainly due to the immigration of immigrants from Cuba, the Dominican Republic and other Latin American countries. In contrast to other southern states of the USA, Florida has a relatively high proportion of Jews, at about 4%.
The main religious communities in 2000:
2,596,148 Catholic Church, 1,292,097 Southern Baptist Convention, 628,485 Judaism, 458,623 United Methodist Church
Largest cities
See also: List of places in Florida

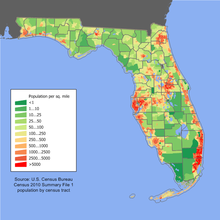
Population density
Questions and Answers
Q: What is the official name of Florida?
A: The official name of Florida is the State of Florida.
Q: How many square miles does Florida cover?
A: Florida covers 65,757.70 sq mi (170,312 km2).
Q: What bodies of water border the state on three sides?
A: The Gulf of Mexico borders the state to the west, the Florida Straits to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
Q: What is the highest elevation in Florida?
A: The highest elevation in Florida is Britton Hill.
Q: What population does it have as of 2015?
A: As of 2015, it has a population over 21 million people.
Q: Who are some ethnicities that live in this state?
A: Some ethnicities that live in this state include Cubans, Haitians and other Caribbeans.
Search within the encyclopedia