Delta wing
![]()
This article or subsequent section is not sufficiently supported by evidence (e.g., anecdotal evidence). Information without sufficient evidence may be removed in the near future. Please help Wikipedia by researching the information and adding good supporting evidence.
Delta wings are the wings of an aircraft with a triangular shape. In addition, aircraft with such wings are also called delta-wing aircraft. The designation was introduced by Alexander Lippisch, who realized in his "Delta 1" a flying wing with relatively high aspect ratio, considerable taper and straight trailing edge. In order to later test the properties of a delta wing with considerably lower aspect ratio, the experimental glider DM-1 was developed. This was taken to the USA after the end of the war and extensively tested in the wind tunnel. Lippisch is generally regarded as the father of the delta wing, although Boris Ivanovich Cheranovsky was researching delta wing aircraft in the Soviet Union at about the same time and successfully flew them (e.g. BITsch-7).
Delta wings are used on supersonic aircraft, including fighter planes and horizontally landing spacecraft.
Low aspect ratio delta wings get additional lift at high angles of attack due to two stable vortices that form along the two leading edges. Thereby the flow partially detaches from the surface. The air in the flow is accelerated by the vortices. Surface is attracted by resulting negative pressure. Upside of each wing-half, air flows within vortex turning inward.
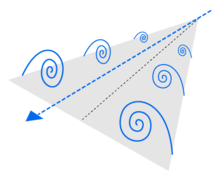
Schematic representation of vortex formation on the delta wing at an angle of attack of 15 °. The blue arrow indicates the direction of flow.

The Avro Vulcan has a delta wing with double bent leading edge

The Convair F-106 has a delta wing with straight leading edge
Special Features
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In contrast to conventional wing geometries (such as rectangular wings, elliptical wings or trapezoidal wings), delta wings on aircraft have the shape of a triangle and thus of the Greek capital letter delta (Δ). They have a relatively small airfoil thickness in relation to their wingspan and depth.
The absence of a complete stall represents a special safety aspect. The decrease in airspeed due to a high angle of attack only leads to a steeper stall and a higher angle of attack in a delta aircraft. Consequently, this can be compensated for by sufficient thrust and the aircraft can be returned to a normal attitude such as straight flight.
Delta wings allow a high lift for a short time, but this is bought with a strong loss of energy. The short-term high lift can be used for fast direction changes or back-fall manoeuvres.
The control flaps on the delta wing can replace the aileron function as well as the elevator, the flaps at the end of the wing are then controlled accordingly mixed. Alternatively or additionally duck wings are used. Also the widespread complete tailplane can be combined with delta wings and duck wings.
Range of use
Delta wings are particularly suitable for the supersonic range. Their shape allows a large area in the Mach cone. In the subsonic range, however, they have a higher drag than conventional wings of greater aspect ratio for the same lift. In the higher supersonic range (Ma ≥ 2), small, thin, trapezoidal stub wings with a negative V-pitch like those of the F-104 offer the better lift-to-drag ratio if the accommodation of hydraulics, landing gear, and integral tank can be dispensed with.
Fighter planes are designed for small turn radii and high roll rates in addition to high speed. For small turn radii or high angular velocity a large lift is required, for high speed a small drag. The delta wing is a suitable compromise; it may be thin, heavily swept, of small span, and of large area. The low aspect ratio results in a lower moment of inertia about the longitudinal axis, which leads to a higher roll acceleration. Its long wing root allows a high torsional stiffness.
The high drag in vortex lift mode was used by the space shuttle to dissipate energy in a controlled manner after re-entry. Fighter planes have sufficient thrust to compensate for the losses.
In the field of aeromodelling delta wings are widely used due to their simple construction and stall resistance.

Double delta at Saab 35 Draken
Search within the encyclopedia





