California
![]()
This article is about the US state. For other meanings, see California (disambiguation).
California (English![]() [kælɪˈfɔɹnjə] and Spanish California [kaliˈfoɾnja]) is a state of the United States. It is the third largest state by area and by far the most populous. California is located in the western part of the country, bordering the Pacific Ocean, the states of Oregon, Nevada, and Arizona, and the Mexican state of Baja California on the peninsula of the same name. California's official nickname is the Golden State.
[kælɪˈfɔɹnjə] and Spanish California [kaliˈfoɾnja]) is a state of the United States. It is the third largest state by area and by far the most populous. California is located in the western part of the country, bordering the Pacific Ocean, the states of Oregon, Nevada, and Arizona, and the Mexican state of Baja California on the peninsula of the same name. California's official nickname is the Golden State.
Geography
California lies at the junction of two tectonic plates called the San Andreas Fault, which is why earthquakes occur frequently throughout the region.
With its area of 423,970 square kilometres, California is the third largest state in the USA after Alaska and Texas. As an independent state, it would be larger than Germany and would rank 59th in the world among the largest states by area, between Iraq and Paraguay. The state stretches over a length of more than 1231 kilometers between 32° 30' N and 42° N and over a width of 400 kilometers between 114° 8' W and 124° 24' W.
Mount Whitney (4418 meters) is the highest mountain in the USA outside of Alaska in California. At the foot of the mountain is the town of Lone Pine, where a famous annual film festival takes place. About 100 kilometers away is the desert area Death Valley ("Valley of Death") with the lowest point in the USA, Badwater, 85.5 meters below sea level. The valley got its name in the time of the first settlers on the West Coast, who not infrequently had to experience the agonies of heat and thirst when they crossed the area. In addition, California is home to numerous natural parks and beaches of varying types. Among the most famous parks is the Yosemite National Park.
Borders
While California is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean on about 1350 kilometers of coastline, it has borders on the continental side with the US states of Oregon in the north, Nevada in the east and Arizona in the southeast, as well as the Mexican state of Baja California in the south.
Geographical regions
The geography of California is extremely diverse relative to the size of the state. There are alpine mountains, foggy coasts, hot deserts, and the fertile Long Valley. California has the tallest coastal redwoods, the thickest giant sequoias, and the oldest awn pines in the world.
The state is often divided into Northern and Southern California. The U. S. Geological Survey defines the geographic center of California as the North Fork in Madera County.
Earth scientists divide the state into eleven distinct geomorphologic areas with clearly defined boundaries. These are, from north to south: the Klamath Mountains, the Cascade Range, the Modoc Plateau, the Basin and Range, the California Coastal Mountains, the Central Valley, the Sierra Nevada, the Transverse Ranges, the Mojave Desert, the Peninsular Ranges, and the Colorado Desert.
Klamath Mountains
The Klamath Mountains are a mountain range in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon. The highest peak is Thompson Peak (2744 m) in Trinity County. The mountains have a very diverse geology with substantial areas of serpentinite and marble rocks. There is limited precipitation in the summer. Because of the geology, they have unique flora, including several endemic plants such as Lawson's false cypress, foxtail pine, the Siskiyou spruce, and Kalmiopsis.
Cascade chain
The Cascade Range is a mountainous region that stretches from British Columbia, Canada, to northern California. The Cascades are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a ring of volcanoes around the Pacific Ocean. All known volcanic eruptions in the United States have come from the Cascades region. The last volcano in California to erupt was Lassen Peak (1921). Lassen is the southernmost volcano in the Cascade Range.
This region is located in northeastern California on the border with Oregon and Nevada north of the Sierra Nevada and Long Valley. The focal point of the area is Mount Shasta near the Trinity Alps. Mount Shasta is a dormant volcano, but there is evidence that it or Shastina, a small neighboring mountain, erupted in the 18th century.
Modoc Plateau
In northeastern California lies the Modoc Plateau, which also extends into parts of Oregon and Nevada.
Large Basin/Basin and Range
The Great Basin is a large, arid, drainageless landscape east of the Sierra Nevada. It lies largely in the neighboring state of Nevada. Basin and Range is the term used to describe a large geologic region dominated by vegetation similar to that of the Great Basin. It also includes the Mojave and Sonora deserts in Mexico.
In the large basin are many larger and smaller mountain ranges and valleys, with Mono Lake the oldest lake in North America, with the Owens Valley the deepest valley on the continent (more than 3000 meters deep, measured from the top of Mount Whitney).
There are a number of dried-up lakes in the Great Basin that were filled with water during the last Ice Age. Many of these lakes have left various salts in the desert landscape, most notably borax, for which Owens Lake and Death Valley are known.
The White Mountains are home to the world's oldest trees, the longleaf pine.
Coastal Mountains
The California Coastal Mountains delineate the California Long Valley from the Pacific Coast and encompass approximately 109,000 square kilometers. They also include the Diablo Range east of San Francisco and the Santa Cruz Mountains south of the city. The coast north of San Francisco is almost always foggy and rainy. The coastal mountains are known for their coast redwoods, the tallest trees on earth.
Californian Long Valley
The California Longitudinal Valley (English Central Valley) is a large, fertile valley between the Sierra Nevada and the Coast Range. Located between 35° and 40° 40' north latitude, the valley has an area of 77,700 km², which is slightly larger than Bavaria. The northern part of the Long Valley is formed by the Sacramento Valley, named after the river of the same name. The southern part is called San Joaquin Valley, also named after the river of the same name. In addition to these two rivers, the Kings River is the larger river flowing through the valley, which is drained by San Francisco Bay. The rivers are sufficiently large and deep that there are several inland ports. There is a seaport at Stockton.
Sierra Nevada
In eastern California lies the Sierra Nevada (Spanish for snowy mountains). The mountain range stretches 600 kilometers from north to south. The highest peak in the heartland of the United States (excluding Alaska and Hawaii) is Mount Whitney (4421 m) near the town of Lone Pine. The topography of the Sierra is characterized by uplift and glaciers.
The Sierra has 200 to 250 days of sunshine a year with warm summers and cold winters, so typical continental climate. The famous Yosemite Valley is located in the central Sierra Nevada. The large and deep freshwater lake Lake Tahoe is located north of the Yosemite National Park. Giant sequoias grow in the mountain range.
Inspired by this beauty, the Sierra Club, a conservation organization, and the American Alpine Club were founded. The latter works to maintain trails, huts, and organized excursions. The Sierra's most famous trail is the John Muir Trail, which runs from Mount Whitney to Yosemite Valley and is part of the Pacific Crest Trail, which runs from Mexico to Canada.
The three largest national parks in this region are Yosemite National Park, Kings Canyon and Sequoia National Park.
Transverse Ranges
The Transverse Ranges (also Los Angeles Ranges) are a mountain range that extends in an east-west direction, rather than north to south as most California mountains do. The Tehachapi Mountains are part of the Transverse Ranges.
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert is a desert in southeastern California. It is about 35,000 km² in size and also covers the territories of Nevada, Utah and Arizona. The Mojave Desert is bounded by the Tehachapi Mountains and the San Bernardino Plateaus. To the west, the desert is clearly delineated by the San Andreas Fault and the Garlock Fault Zone.
Peninsular Ranges
The southernmost mountains in California are the Peninsular Ranges, which extend east from San Diego and into Mexico's Lower California Peninsula. The Peninsular Ranges include the Sierra San Pedro Mártir in Mexico. The Peninsular Ranges include the Laguna Mountains, the San Jacinto Mountains, the Santa Ana Mountains, and the Palomar Mountain Range, best known for the Palomar Observatory.
Colorado Desert
The Colorado Desert is about 39,000 km² in size and is located in southern California and Mexico. A feature of the desert is the Salton Sea. It was first formed in 1905, when a dam of the Colorado River broke and the water masses crashed into the dry area. Today, the Salton Sea is the largest lake in California, near the border with Mexico. The desert forms the remnant of a former ocean bay, which today lies up to 100 meters below sea level.
Climate
The climate in California can be divided into three zones:
- On the coast, temperatures are lower than in the interior of the country due to the influence of the rather cool Pacific Ocean. In the north there are often rainy winters. In addition, there is often fog in the summer, which provides correspondingly cooler temperatures.
- In mountains like the Sierra Nevada, it often gets quite hot in summer, but due to the altitude, temperatures drop quickly after sunset. In winter, very large amounts of snow must be expected.
- In the desert it is mostly sunny and warm during the day all year round, but at night it cools down very much.
California is also known as the "Fruit Belt of America," with a climate ideal for growing grapes, oranges, lemons and avocados.
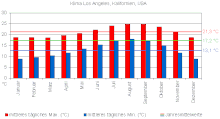
Climate in Los Angeles

Mount Whitney
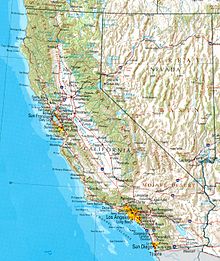
Geographical map of California

Pacific coast near Big Sur

Mojave Desert
Demographics
The population of California is rising sharply. Since 1962 it has been the most populous US state, today it already has twice as many inhabitants as New York, which until then was the most populous. Along with Texas, New Mexico and Hawaii, California is one of four so-called majority-minority states, i.e. states in which non-Hispanic whites make up less than 50% of the population. More than 200 languages are spoken in California, with Spanish being the most widely spoken language after English. Spanish is especially common in Southern California, where Hispanic immigrants are particularly prevalent due to the border with Mexico.
Demographic projections predict that California will have a Hispanic majority population by 2020, due to both higher birth rates and higher immigration rates.
California is the second most populous (member) state in the Western Hemisphere, surpassed only by the state of São Paulo. If California were its own country, it would be the world's 34th most populous state in terms of population, ahead of Canada and Australia, which are significantly larger in area.
Population
California had a population of 37,253,956 as of the 2010 census. Between the years 2000 and 2010, the population grew by 3,382,308, a 10% increase. As of mid-2017, the population is estimated by the US Census Bureau to be 39,536,653. About 12% of all U.S. residents live in California.
California is home to eight of the 50 largest cities in the country. Los Angeles is the second largest city in the United States with a population of 3,792,621 (Census 2010), followed by San Diego (8th), San Jose (10th), San Francisco (14th), Fresno (35th), Long Beach (36th), Sacramento (37th) and Oakland (45th).
Also, one of the North American cultural areas used to divide the Native American population by (mostly historical) cultural characteristics is called "California." Although the California Indians have only very small reservations, many of them are anxious to preserve their traditions.
See also: List of cities in the United States by number of inhabitants
Age structure
The age distribution of California is as follows:
- up to 18 years: 9,531,046 (26.1 %)
- 18 to 64 years: 22,998,673 (63.1 %)
- 65 years and older: 3,927,830 (10.8 %)
The median age is 34.4 years.
Origins
California has a population of 37,253,956 (as of the 2010 U.S. Census), of which 61.6% are white, 14.9% are Asian, 7.2% are black and African American, 1.9% are Native American, and 0.8% are Hawaiian (multiple responses were allowed). Regardless of "race," 37.6% identify as Hispanics. There are 12,577,498 households.
California has the largest number of white Americans in the United States, 22,953,374. The state has the fifth largest African American population in absolute numbers (2,683,914). Approximately 5.56 million citizens of Asian descent live in California, which is about one-third of the total Asian population in the United States. Native Americans are also more prevalent than in any other state, with 723,225 people.
According to 2006 estimates, 57 % of the population belong to minorities. The percentage of non-Hispanic white population dropped from 80% (1970) to 43% now. Only New Mexico and Texas have higher percentages of Hispanics, but California has the most in absolute numbers. Hawaii is the only state with a higher percentage of Aso-Americans than California. Specifically for Japanese and Chinese Americans, New York just replaced California as the largest state.
25% of the population is of Mexican descent. Mexico is the largest country of origin for Californians. They make up the largest group within the population of Hispanic/Latino descent, totaling 32.4% of the total population.
Just under 10.0% of residents are of German descent, making them the largest group within the white population, which accounted for 59.5% of the total population in Census 2000. This is followed by the Irish (7.8%), English (7.1%) and Italian (4.3%) groups.
Mexican-Americans live primarily in Southern California. Los Angeles is the largest Mexican community in the U.S. since 1900. The Imperial Valley on the border with Mexico also has a high percentage (70 to 75%) of Latinos. Riverside County has a high Hispanic population, especially in the east. Many Hispanics also live in the Long Valley and the San Francisco Bay Area.
Most Hispanics are of Mexican background, although many are from Central America, the Caribbean (Cuba or Puerto Rico), or South America. In Los Angeles County, Hispanics make up 40% of the population.
By about 2020, Hispanics will be the majority population in California. Some demographers assume that California, along with the entire southwestern United States, will become Latino-majority Spanish-speaking territory. Other demographers, however, assume that Hispanics in the United States will integrate like the other immigrant groups and become English-speaking and assimilated after the third generation at the latest.
Population development
| Population development | |||
| Census | Inhabitants | ± in % | |
| 1850 | 92.597 | - — | |
| 1860 | 379.994 | 310,4 % | |
| 1870 | 560.247 | 47,4 % | |
| 1880 | 864.694 | 54,3 % | |
| 1890 | 1.213.398 | 40,3 % | |
| 1900 | 1.485.053 | 22,4 % | |
| 1910 | 2.377.549 | 60,1 % | |
| 1920 | 3.426.861 | 44,1 % | |
| 1930 | 5.677.251 | 65,7 % | |
| 1940 | 6.907.387 | 21,7 % | |
| 1950 | 10.586.223 | 53,3 % | |
| 1960 | 15.717.204 | 48,5 % | |
| 1970 | 19.953.134 | 27 % | |
| 1980 | 23.667.902 | 18,6 % | |
| 1990 | 29.760.021 | 25,7 % | |
| 2000 | 33.871.648 | 13,8 % | |
| 2010 | 37.253.956 | 10 % | |
| Estimate 2017 | 39.536.653 | 6,1 % | |
| Before 1900 1900–1990 2000 + 2010 | |||
California has been the most populous state in the United States since 1962, when it replaced New York. Since then, the population has more than doubled again, largely due to the change in laws governing immigration to the United States, in addition to economic dynamism.
Languages
According to the United States Census 2000, 60.5% of Californians speak English and 25.8% speak Spanish as their native language. High Chinese is in third place with 2.6% of speakers, followed by Tagalog (2.0%) and Vietnamese (1.3%). In total, more than 200 languages are spoken in California.
More than 100 Native American languages are spoken in California. Many of them are endangered, but there are efforts to revitalize them.
English has been the official language under the Constitution since 1986. Language policy is an important issue in California.
Religions
In absolute numbers, the most Catholics in the US and the second most Mormons after Utah live in California. The state has one of the largest Jewish communities in the western US, clustered mainly in Los Angeles, Beverly Hills, San Francisco, Oakland, Sacramento and Palm Springs. The number of Muslims in California is about one million.
Most Catholics are descended from Irish, Italians, Hispanics and Filipinos. Immigration of Latin Americans and Filipinos has recently increased the number of Catholics in California. While the percentage of Catholics among the black population is low, as they are mostly from the Protestant southern states, it is highest among Hispanics.
Due to the high percentage of Aso-Americans, there are numerous Asian religions in California such as Hinduism, Buddhism and Taoism.
The religious denominations with the largest number of members in 2000 were the Roman Catholic Church with 10,079,310, Jewish congregations with 994,000 members, the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 529,575, and the Southern Baptist Convention with 471,119 adherents.
- Protestants - 33 %
- Baptists - 4 %
- Presbyterian - 3 %
- Methodists - 2 %
- Catholics - 31 %
- Jews - 3 %
- Mormons - 2 %
- Muslims - 1 %
- Other - 4
- Non-religious - 21 %
According to a Pew Research Center survey, Californians are less religious than the populations of other states in the US. Of those surveyed, 62% said they are strongly religious, compared to 71% nationwide. Further, religion is important to 48% of Californians, while 56% of Americans say this.
big cities
See also: List of cities in California by number of inhabitants
The largest city in California is by far Los Angeles, which is also the second largest city in the USA. With 17.8 million inhabitants, the metropolitan region around Los Angeles is one of the largest on earth. Other major cities are San Francisco and San José, both of which are part of the San Francisco Bay Area, a metropolitan area of about 7.5 million people around San Francisco Bay.
With about 1.3 million residents and about three million in the metropolitan area, SanDiego, located in Southern California, is the second largest city in California and the third largest metropolitan area in the state.
Sacramento, the capital of California since 1854, is located at the level of San Francisco Bay about 120 km inland. Sacramento itself has just under 500,000 inhabitants, and about two million people live in the metropolitan area.
Other major cities include Oakland and Berkeley, both located in the San Francisco Bay Area, as well as Santa Barbara, Modesto, Fresno, Bakersfield, and Stockton. Also significant are Ventura, Anaheim, Long Beach, Irvine, Santa Ana, Riverside and San Bernardino, all located in the Los Angeles metropolitan area.

.jpg)
Sacramento

San Francisco

San Diego

Los Angeles

The Wilshire Boulevard Synagogue in Los Angeles
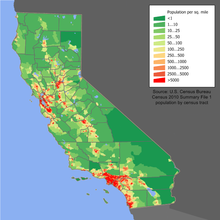
Population density, in square miles (1 mi²= 2.6 km²)
Questions and Answers
Q: What is the capital of California?
A: The capital of California is Sacramento.
Q: How many people live in California?
A: As of 2019, over 39 million people live in California.
Q: What are the largest cities in California?
A: The largest cities in California are Los Angeles, San Diego, San Jose, and San Francisco.
Q: What state borders California to the southeast?
A: Arizona borders California to the southeast.
Q: Who were the first settlers of what is now known as California?
A: Native Californian tribes were the first settlers of what is now known as California.
Q: What percentage of people living in California are Hispanic?
A: Approximately 39% of people living in California are Hispanic.
Q: Where do most immigrants living in California come from?
A: Most immigrants living inCalifornia come from Mexico (3.9 million), followed by the Philippines (859,000), China (796,000), Vietnam (539,000), and India (513,000).
Search within the encyclopedia