Adder (electronics)
A full adder is a switching network that is usually realised as a digital circuit. It consists of three inputs ( 








The following truth table shows how a full adder works:
This results in the following equations by first forming the disjunctive normal form from the truth values of the table and then simplifying:
and
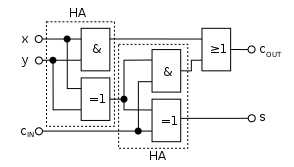
The illustration on the left shows the construction of a full adder using half adders and an Oder gate.
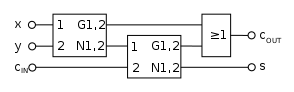
The figure on the right also shows the structure of a full adder, whereby the half adders have each been separated into an AND gate and an exclusive OR gate. Note that in both figures the sum outputs 

Further optimising the expression for the full adder without slowing down the carry path results in further simplifications:

The full adder is used to build adders and multipliers, often with a half adder at the beginning of the carry chain.
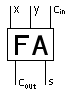
Circuit symbol of a full adder
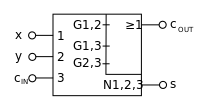
Switching symbol of a full adder according to DIN 40900
Structure of a full adder with two AND, two XOR and one OR gates according to DIN 40900
Construction of a full adder by means of two half adders and an Oder gate according to DIN 40900
Search within the encyclopedia


