Xhosa language
![]()
This article or section is still missing the following important information:
Concrete presentation of phonetics and phonology (in IPA), grammar, vocabulary, spelling (table of the alphabet), examples (the text of a song highlighting a particular phonetic feature, as well as some tourist phrases are rather unsuitable); literature (scientific literature, not just a phrasebook for tourists!); cf. format template language.
Help Wikipedia by researching and adding them.
isiXhosa ( ![]() , German pronunciation: [iziˈkoːza]), simplistically called Xhosa (isi- is a singular prefix, the latter being obligatory for nouns in Bantu languages), is the Xhosa language and one of the eleven official languages in the Republic of South Africa; it is also spoken in Botswana and Lesotho.
, German pronunciation: [iziˈkoːza]), simplistically called Xhosa (isi- is a singular prefix, the latter being obligatory for nouns in Bantu languages), is the Xhosa language and one of the eleven official languages in the Republic of South Africa; it is also spoken in Botswana and Lesotho.
It is spoken by about nine million people. It is the second most widely spoken mother tongue in South Africa after isiZulu and is used as a first language by 15.43 per cent (as of 2015) of the population over the age of 15.
The snapping sounds are particularly characteristic; the name Xhosa also begins with a snapping sound. It is written in the international phonetic alphabet as follows: [ǁʰosa].
isiXhosa is a southeastern Bantu language of the Nguni subgroup, but about 15 percent of its vocabulary comes from the Khoisan languages. It is closely related to isiZulu, the Zulu language.
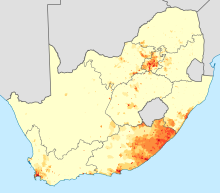
Density of isiXhosa speakers in South Africa (2011)
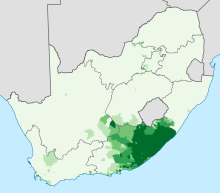
Proportion of isiXhosa speakers in South Africa (2011)
History
The name Xhosa comes from a legendary chief. The ethnic group that speaks isiXhosa refers to itself as the amaXhosa. Almost all languages with clicks are Khoisan languages and the presence of these clicks reveals the close historical links with neighbouring Khoisan languages.
Geographical spread
The language represents the most south-western part of the Nguni family, a sub-family of the Bantu languages. Most native speakers live in the Eastern Cape Province, but there are also increasing numbers of speakers in the Western Cape Province, including Cape Town.
Search within the encyclopedia