Vacuole
Vacuoles are cell organelles. They are constructed similarly to vesicles, but comprise much larger spaces enclosed by a membrane. Due to their size, they are also visible under the light microscope. They appear, for example, as food vacuoles formed by phagocytosis from parts of the cell membrane.
The cell sap vacuole (also called central vacuole or cell sap space) is particularly conspicuous. It usually occupies the largest volume of the cell in mature plant cells. The membrane that separates the vacuole from the adjacent cytoplasm is called the tonoplast. Inside the vacuole is a fluid, the cell sap, which, unlike the cytosol, contains very few proteins and is therefore not plasmatic. Vacuoles can have the following functions:
- Generation of a bulging state of the cell by the turgor
- Substance stores of proteins, organic compounds and ions, i.e. substances that could have a toxic effect or disrupt the metabolism.
- By storing toxic or bitter substances, they can protect themselves from animal damage or fungal attack (e.g. calcium oxalate crystals).
- By storing dyes in the cell sap, plant parts can be specially coloured: blue-violet-red are often anthocyanins, which form red salts with acids and blue salts with bases (flowers of hollyhock, cornflower, hydrangea), yellow are flavones (flowers of primroses, snapdragons).
- They also play a role in growth and movement processes through osmotic uptake of water into the vacuole
- digestion of macromolecules (cf. lysosomes in animals)
- storage function - for example in legumes, in whose cotyledons vacuoles with storage proteins are found.
- Tannins form a disinfectant layer when wounded and cause the proteins of the cytoplasm to stagnate (wound closure)
The formation of a vacuole takes place during cell growth. Within the elongation growth of the plant cell, the volume of the cell increases by osmotic water uptake. However, since the substance of the cytoplasm does not grow fast enough, voids are formed which are subsequently separated from the adjacent plasma by tonoplasts. At the end of growth, the central vacuole often occupies such a large space that the cytoplasm only forms a thin layer between the plasmalemma and the tonoplast. This is how the central vacuole is formed.
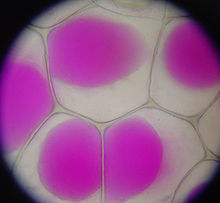
... if it does not fill the whole cell (plasmolysis).
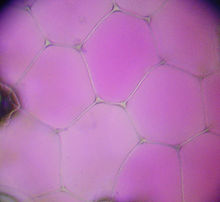
The central vacuole of the purple-leaved three-master flower (Tradescantia spathacea) is easier to see ...
See also
- Contractile vacuole
- Food vacuum
- Vesicle (Biology)
- Lysosome
Questions and Answers
Q: What is a vacuole?
A: A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle, which is a kind of vesicle. It is a closed sac made of membranes with inorganic or organic molecules inside, such as enzymes.
Q: What shape and size do vacuoles have?
A: Vacuoles have no set shape or size, and the cell can change them as needed.
Q: How important are vacuoles in different types of cells?
A: The importance of vacuoles depends on what kind of cell they are in. They are much more important in plant and fungus cells than in animal cells.
Q: What are some common jobs that vacuoles do?
A: Some common jobs of a vacuole are to hold waste products, keep things separate from the rest of the cell, hold water in plant cells, keep the internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor steady in a cell, keep an acidic pH on the inside of a cell, hold small molecules, store proteins for seeds to sprout and help with autophagy and destroying broken proteins that build up in cells.
Q: How do protists use their vacuoles?
A: In protists, vacuoles also store and help digest food that the protist ate.
Q: Are protein bodies similar to normal vacuoles?
A: Yes, protein bodies are just slightly different from normal vacuoles. They contain proteins that seeds use to sprout when planted.
Q: Can some kinds of vacuules act as houses for symbiotic bacteria? A:Yes ,some kinds of vaccules may act as houses for symbiotic bacteria .
Search within the encyclopedia