Unix
Unix (English [ˈjuːnɪks]) is a multi-user operating system for computers. It was developed in August 1969 by Bell Laboratories to support software development. Today, Unix is generally synonymous with operating systems that either originated in AT&T's (originally Bell Laboratories) Unix system or implement its concepts. It, along with its variants and advancements-often under other, more publicly known names-is one of the most widespread and influential operating systems in computer history. Until the 1990s, Unix was mainly used in specialized application areas such as workstations and servers, especially at universities and research institutions. Today's mass adoption in almost all areas of computing did not begin until around the 2000s.
The main developers of Unix were Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie, who first wrote it in assembly language, then in the C programming language developed by Ritchie. Unix introduced some key concepts of information technology for the first time, such as the hierarchical, tree-like file system with folder structure. The early developers also defined a set of concepts and rules for software development that became known as the Unix philosophy. Unix was further developed as an open-source operating system until the 1980s, primarily at US universities, and had a considerable influence on hacker culture.
It was commercialized by AT&T in the 1980s, leading to a series of independent advancements and spin-offs, and resulting in the so-called "Unix Wars" between various systems and vendors. Today, the various operating systems based on or derived from Unix are collectively the most widely used operating systems for computers and for many types of electronic devices that contain a computer. These range in use from mobile devices such as smartphones to personal computers and web servers to the largest supercomputers. Furthermore, the Unix-like Linux in particular is also used as an embedded system in industrial measurement and control devices, in medical technology devices, consumer electronics and electronically controlled consumer goods such as household appliances, motor vehicles or WLAN routers. The most widespread commercial, proprietary Unix variant today is Apple's macOS and its mobile variant iOS, while the most widespread Unix-like open source variant is Linux and its derivative Android.
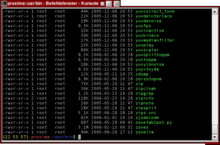
Typical Unix input window for command line commands, also called terminal or Unix shell. Shown is the listing of the contents of a folder after entering the Unix command ls -l
Variant typology
Since the term "UNIX" in capital letters or "UNIX" in small caps is a registered trademark of the Open Group, only certified systems may use the name UNIX. Accordingly, "UNIX" is commonly used in technical literature to denote certified systems, while "Unix" is used to denote all Unix-like systems.
Unix-like systems can be divided into UNIX derivatives and unixoid systems. UNIX derivatives include, for example, the BSD systems, HP-UX (Hewlett-Packard), DG/UX (Data General), AIX (IBM), IRIX (Silicon Graphics), UnixWare (SCO Group), 386/ix (first Eastman Kodak, later SunSoft), Solaris (Oracle), AMIX (Commodore), and macOS (Apple).
Other systems such as Linux or QNX, on the other hand, are not based on the original Unix source code, but were developed separately. They are called "unixoid systems" because they also implement a part of the operating system functions (POSIX) defined in a standardized way for Unix. A special case is BSD, which was originally based on Bell Labs source code, but since the mid-1990s has been completely rewritten by a loose community of programmers, so that it is now free of the original, proprietary program code.

Typical graphical user interface of a Unix-like system, based on the widely used X Window System.
Distribution
Originally mainly used in the university sector, from the 1980s and 1990s it was mainly used in professional workstations and on servers. With Linux, macOS (until 2016 OS X and originally, until 2012, Mac OS X) and as the basis of several widespread operating systems for mobile devices, it also reached the mass market for home users from around the 2000s. The two most widely used operating systems for smartphones and tablet computers, iOS and Android, are based on unixoid operating systems with BSD (iOS) and Linux (Android), respectively. As of September 2013, over one billion Android devices alone were activated worldwide. For 2013, the market research company Gartner Group predicted that, for the first time, more Android-based systems would be sold than PCs with Windows. In addition, Linux gained greater importance as an open source operating system for corporate applications and as an embedded system for electronic devices such as WLAN routers or consumer electronics devices.
Since the Unix-like Linux can be very flexibly adapted and optimized, it has also become widespread in data centers, where specially adapted versions run on mainframes, computer clusters (see Beowulf) or supercomputers. The systems listed in the TOP500 list of fastest computer systems are currently (as of November 2018) run exclusively on Linux. Windows, the biggest competitor in the desktop sector, does not play a role in the supercomputers.

Professional computer graphics and CAD workstation SGI Octane with the UNIX derivative IRIX, late 1990s.

IBM Blue Gene
Questions and Answers
Q: What is UNIX?
A: UNIX is a computer operating system that was first developed in 1969 at Bell Labs.
Q: Who created UNIX?
A: Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Douglas McIlroy, and others created it.
Q: How was UNIX written?
A: It was written using assembly language.
Q: What does the Unix operating system allow for?
A: The Unix operating system allows for multiple users and processes to run simultaneously on the same machine or network of computers.
Q: What is the "Unix philosophy"?
A: The "Unix philosophy" refers to the idea that many other operating systems have copied ideas from Unix, leading to its influence being seen across many different types of systems.
Q: Is Linux a type of UNIX?
A: No, Linux does not use code from UNIX but instead shares some of the ideas and commands which makes it a "Unix-like" system rather than an actual UNIX system.
Q: What are two ways to use a Unix system?
A: Two ways to use a Unix system are with the command line interface or with a graphical user interface (GUI).
Search within the encyclopedia