Ulcer (dermatology)
![]()
This article is about the medical term. In botany, ulcer is a form of aperture in pollen grains.
Ulcus or ulcer (plural ulcers or ulcera), German Geschwür (from Middle High German geswër, "ulcer, abscess, tumour", related to Schwär from Middle High German swër "physical pain, disease, ulcer, tumour"), in medicine refers to a "deep-seated substance defect" of the skin or a mucous membrane which is not traumatic but e.g. of infectious, ischaemic or immunological aetiology (origin). The term "wound", on the other hand, also includes substance defects of traumatic origin.
More superficial defects are called erosion (the upper epidermal layers are affected here) or excoriation (all layers of the epidermis affected, i.e. including the basement membrane), see also efflorescence. Such defects may also be of traumatic origin (for example, abrasions). What breaks through the basement membrane (the boundary between epidermis and dermis) is generally called a deep wound - or an ulcer in case of atraumatic origin.
Because the presence of an intact basal cell layer (stratum germinativum, a single-layer epithelium attached to the basal membrane) is necessary for scarless healing, scarless healing is no longer possible in the case of ulcers, in contrast to the more superficial defects.
The development of an ulcer is called ulceration. The cause may be circulatory disorders, infections (possibly with secretion of pus) or tumours or a combination of these factors (e.g. in diabetes mellitus). Ulcerations are frequently symptoms of general diseases and often occur in multiples.
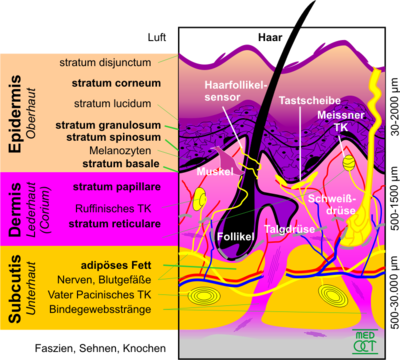
Structure of the skin
Common forms
- Ulcus cruris (open leg, lower leg ulcer, usually due to venous or mixed arterial-venous insufficiency)
- Malum perforans (pressure sore on the feet in polyneuropathy)
- Ulcus (cruris) hypertonicum (Martorell syndrome)
- Ulcus ventriculi (stomach ulcer, more precisely: stomach wall ulcer)
- duodenal ulcer (ulcer of the duodenum)
- Pressure ulcer (decubitus) in case of reduced perfusion of the tissue due to chronic pressure effect
- Ulcus durum (hard chancre), the primary effect in syphilis
- Ulcus molle (soft chancre), a sexually transmitted disease
- Radiation ulcer or ulcus radiologicum
- Ulcus carcinomatosum (cancerous ulcer)
- Ulcus rodens or ulcus terebrans in the case of basal cell carcinoma
- Corneal ulcer (corneal ulcer)
- Aphtae (ulceration of the oral mucosa or gums)
- Ulcus arteriosum (arterial ulcer)
- Ulcus venosum (venous ulcer)
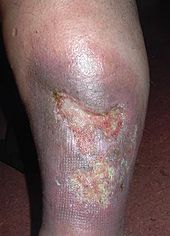
Untreated leg ulcer
Search within the encyclopedia