Treaty of Rome
The Treaty establishing the European Community (EC Treaty, or TEC) was renamed the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union by Article 2 of the Treaty of Lisbon with effect from 1 December 2009.
Originally, the Treaty was called the Treaty establishing the European Economic Community (EEC Treaty). The Treaty of Maastricht in 1992 renamed the EEC Treaty the EC Treaty and the Treaty of Amsterdam in 1997 renumbered it. The renamings were accompanied in each case by substantial changes to the Treaty.
The EEC Treaty established the European Economic Community. It was concluded for an unlimited period of time. The Treaty is one of the primary sources of law within European law. With the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon on 1 December 2009, the European Community was merged with the former European Union; they continue to exist as a single legal entity under the name European Union.
The EEC Treaty and the Treaty establishing the European Atomic Energy Community (EURATOM), also signed in 1957, are known as the Treaties of Rome.
The first signatories were the representatives of Belgium, the Federal Republic of Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg and the Netherlands in Rome on 25 March 1957. The contents of the treaty had been worked out in advance at the Bilderberg conferences. It entered into force at the beginning of 1958 after the deposit of the last instrument of ratification (according to Art. 313 with the government of the Italian Republic).
Later, the following states joined the treaty:
- Kingdom of Denmark, Hellenic Republic, Kingdom of Spain, Republic of Ireland, Republic of Austria, Portuguese Republic, Republic of Finland, Kingdom of Sweden, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Republic of Estonia, Republic of Latvia, Republic of Lithuania, Republic of Poland, Czech Republic, Slovak Republic, Republic of Hungary, Republic of Slovenia, Republic of Malta, Republic of Cyprus, Romania, Republic of Bulgaria and Croatia.
The EC Treaty represented the continuation of the drive for cooperation in Europe in certain sub-areas following the Second World War and the establishment of the Coal and Steel Community. This was preceded by attempts to establish a defence community (EDC Treaty), which failed, however, because the French National Assembly (Parliament) voted against voting on the intended treaty by 319 votes to 264. This was followed by the realisation that European integration in the economic field would initially be easier to advance.
The main provisions of the European Coal and Steel Community Treaty (ECSC, Coal and Steel Community) were transferred to the EC Treaty after its expiry in 2002.
The usual abbreviation is TEC, but when citing individual articles, the European Court of Justice wanted the abbreviation EC to be used when citing according to the current numbering (TEC with old numbering), e.g. "Art. 81 EC" (formerly "Art. 85 TEC"). This abbreviation has therefore become established in many journals, but not everywhere, even in the EU institutions. If no individual provision is cited, however, it must in any case be called ECT, because EC is the abbreviation for "European Community(ies)".
The treaty has a supranational normative character and has priority of application, but no priority of validity over national regulations. With the "Solange II Decision" of the Federal Constitutional Court, this construction was also recognised under constitutional law.
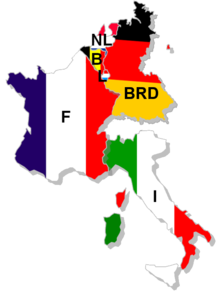
Founding members of the EEC

Room in the Musei Capitolini where the Treaties of Rome were signed (photo 2004)
Timetable of the European Treaties
| Subz. | 19481948 | 19511952 | 19541955 | 19571958 | 19651967 | 19861987 | 19921993 | 19971999 | 20012003 | 20072009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||
| European Communities | Three pillars of the European Union | ||||||||||||||||||||
| European Atomic Energy Community (EURATOM) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) | Contract expired in 2002 | European Union (EU) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| European Economic Community (EEC) | European Community (EC) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| Justice and Home Affairs (JHA) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
| Police and judicial cooperation in criminal matters (PJCC) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| European Political Cooperation (EPC) | Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Western Union (WU) | Western European Union (WEU) |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
| dissolved as of 1 July 2011 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Search within the encyclopedia