Transgender
![]()
The articles transgender, transsexuality and transidentity overlap thematically. Information you are looking for here may also be found in the other articles.
You are welcome to participate in the relevant redundancy discussion or directly help to merge the articles or better distinguish them from each other (→ instructions).
Transgender (indeclinable adjective transgender, composed of Latin trans "beyond, beyond", and English gender "social gender") is a designation for persons whose gender identity does not correspond or does not correspond completely with the sex registered after birth on the basis of external characteristics, or who reject a binary assignment. The increasing use of the term transgender shows a move away from the heteronormative concept of transsexuality that has been dominant in jurisprudence and legislation until now and that focuses on physical unambiguity, the pathologizing context of which was shaped by medicine and sex research in the 1970s. In distinction to this, we also speak of transsexuality, transidentity and trans*. These terms serve as a generic term for describing oneself or others, as well as for defining the position of transgender persons with a female (transwoman) or male (transman) gender identity and all forms of identity in between. Increasingly, transgender is experiencing a broadening of meaning, according to which identity concepts outside the norm of bisexuality are also included in the spectrum of meaning of "transgender" (see non-binary, genderqueer gender identities, such as genderfluid, bigender, pangender, gender-neutral).
Transgenderness is independent of sexual orientation. People who are transgender can be heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual or asexual, or they can refuse to specify their sexuality.
The opposite of transgender is cisgender (Latin cis "this side", as an opposite preposition to trans). It describes people whose sex or gender identity and gender expression is the same as the sex they were assigned at birth.
The degree to which individuals are comfortable with their physical appearance and embrace their authentic identity has also been termed transgender congruence. Many transgender individuals experience gender or gender dysphoria, and some therefore seek medical intervention, such as hormone therapy and gender reassignment surgery. But not all transgender people want or are able to take advantage of these measures, for example for medical reasons.

Transgender Pride flag : white represents transgender, non-binary and intersex people
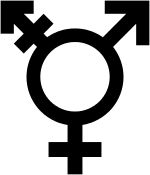
The transgender symbol as a combination of the Venus and Mars symbols with an additional "arm" for transgender persons.
Frequency
A June 2016 Williams Institute study on how many adults in the U.S. identify as transgender found the population to be 0.6%.
The frequency in Germany can be derived from the case figures of the Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection (BmJV). The business load at courts and public prosecutors' offices in the area of voluntary jurisdiction shows about 29,700 proceedings according to the Transsexual Act (TSG, proceedings for change of name and civil status) for the period 1981 to 2019. The number of cases has been increasing for years and is currently (2019) at 2582 (2018: 2614, 2017: 2085, 2016: 1,868, 2015: 1648) per year. This does not include people who consider themselves to be transgender, transsexual or transident, but who do not wish to be classified in one of the two available genders according to the TSG and therefore could not file an application under this law until 22 April 2020 (BGH XII ZB 383/19, RN 53). A frequency of 1:298 (0.336 % of the total population) results if one puts the annual number of cases in relation to the annual number of births (in 2019 this was 778,090). The Transsexual Act has been open to people without a desire for medical gender reassignment surgery since 2011.
In spring 2020, 2.1% of 50,300 undergraduates in the U.S. answered in the affirmative to the question, "Do you identify as transgender?" (1,055 people); 97.9% answered "no." A total of 3.7% or 1,844 students reported being non-binary; 57% of them had answered "transgender" in the affirmative (details). In response to the question, "What gender were you assigned at birth?", 68.4% of all respondents were female, 31.6% were male, and 19 individuals (0.038%) were intersex. The online survey was conducted as an annual study by the two U.S. student health organizations, American College Health Association (ACHC) and National College Health Assessment (NCHA), and had a response rate of 14%.
Basics
The term transgender was originally a designation for people who identify with their original biological sex only insufficiently or not at all and feel their biological sex to be wrong.
Transmen are people who were assigned the female gender at birth but identify as men. Transwomen, conversely, are people who identify as women despite being initially assigned the male gender. While many transgender people clearly identify with one gender, others reject any clear form of gender assignment or categorization for themselves.
By some groups transgender is meanwhile also used as a generic term for all persons who evade a clear gender assignment. They define transsexuality and transvestitism as well-known sub-concepts to this umbrella term. However, occasionally some other non-transsexual people are also referred to as transgender who live permanently or predominantly in or empathize with a different gender role. These include, for example, androgyny, cross-dressing, dragking, or drag queen.
The last three manifestations are considered transgender if the transgression of the gender role is not only to be seen as travesty in the sense of a publicly displayed disguise art. Usually transvestite fetishism is not included, in which the change of gender roles only happens temporarily and serves a sexual stimulation, however, in individual cases the demarcation can be difficult.
Whether and to what extent transgender persons seek medical gender reassignment varies from case to case, but this is or was often considered a necessary condition for a legal change of first name or civil status.
The opposite of transgender is cisgender (Latin cis "this side", and English gender "social sex"). This term evolved from the term cissexuality, coined by sexologist Volkmar Sigusch, to describe people whose gender identity matches their innate biological sex.
Search within the encyclopedia