Topography
Topography is the branch of national surveying or cartography that deals with the detailed surveying, representation and description of the earth's surface and the natural and artificial objects (situation) that are firmly connected to it. Of greatest importance are the terrain and its forms (relief), water bodies, land use and vegetation, as well as buildings and traffic routes.
The name comes from the Greek τόπος tópos ("place") and γράφειν gráphein ("to draw, to write") and literally means "description of a place" or "sketch of the terrain".
Topographic or terrain surveys are carried out by topographers and/or surveyors. The measurements are made terrestrially (with tachymeter, GPS/GNSS or earlier with the survey table, compass and slope meter) or with the help of aerial photographs (less frequently satellite images). Terrestrially, the terrain is surveyed point by point, supported by structure lines. From aerial photographs (aerofotogrammetry) it is possible to determine the course of contour lines in the terrain in addition to surveying objects.
The results are presented in topographic maps (maps) or a cartographic relief, or according to more recent methodology as a digital landscape model. On the other hand, the pure elevation representation of the terrain is referred to as a digital elevation model, and its addition of buildings, pipelines, etc. as a land information system (LIS).
In geography, the term topography is often used in the sense of orography, i.e. the mapping of the terrain with its elevation structures and water bodies.
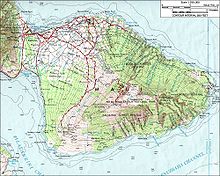
Topographic Map of Maui (Hawaii)
See also
- Mapping (cartography)
- Terrestrial photogrammetry
- Terrain profile
Search within the encyclopedia